Claude 3.7 Sonnet has quickly become one of the most powerful multimodal models available for computer vision tasks, combining strong reasoning capabilities with the ability to understand and analyze visual content. Now, with Roboflow's fine-tuning/prompting capabilities, you can customize this model specifically for your domain - whether that's medical imaging, retail analytics, manufacturing quality control, or any other specialized application.
In this guide, we’ll be fine-tuning 3.7 Sonnet with JSON structured outputs, and building a tool that can recognize fruits and do visual-questioning answering for various details.
Let’s get started!
You might also be interested in trying Claude 3.7 Sonnet against other models in the model playground.
Fine-Tune Claude 3.7 Sonnet for Computer Vision
Get a Claude API Key
To be able to use Claude 3.7 Sonnet, we’ll need an Anthropic API Key. To get one, head to the Claude Console for developers, and log in/create an account. Heading over to the console:
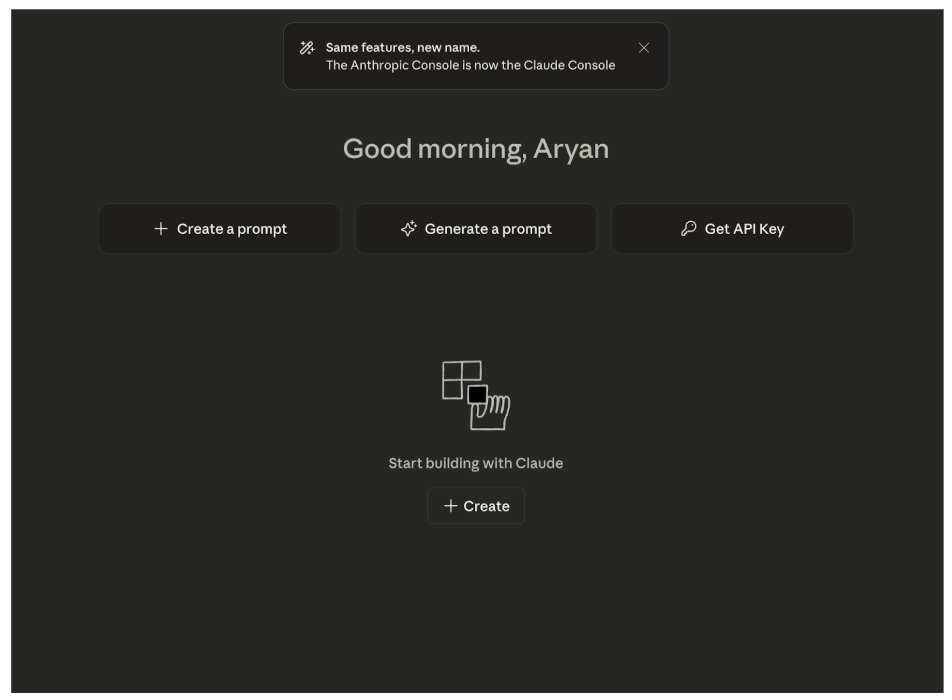
From here, you can generate a new API Key. Make sure to keep note of this key somewhere, because once you close the window, the console will not show the same key again.
Build a Workflow
Next we’ll build a workflow with Claude using Roboflow. Head over to Roboflow, and log in/create an account. From there, create a workspace, and enter the Workflows tab:
Then, create a new workflow with the “build my own” option:
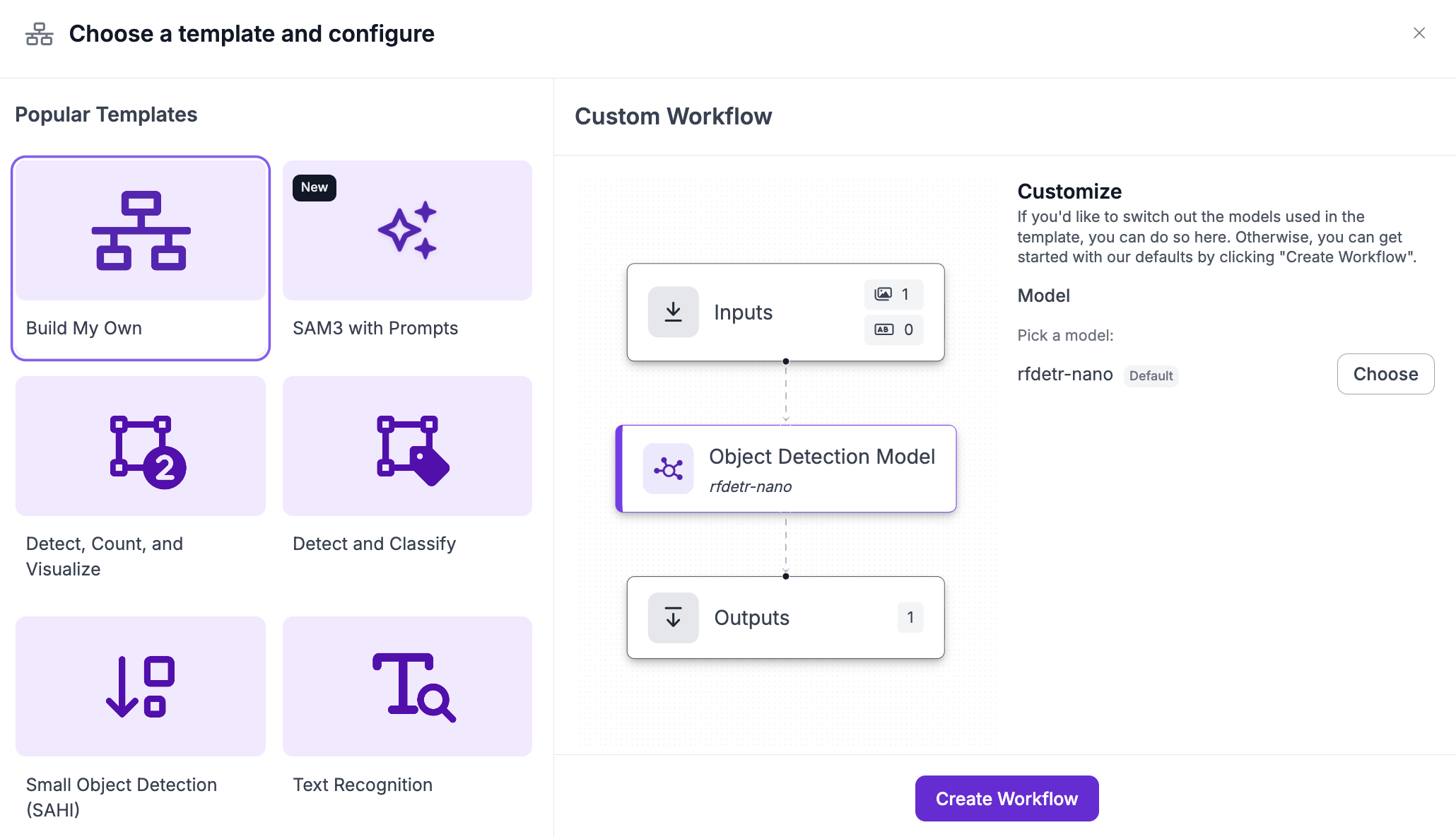
In the workflow, get rid of the default object detection model, and search for the Anthropic block:
From here, select Claude 3.7 Sonnet as the model and add the Anthropic API key:
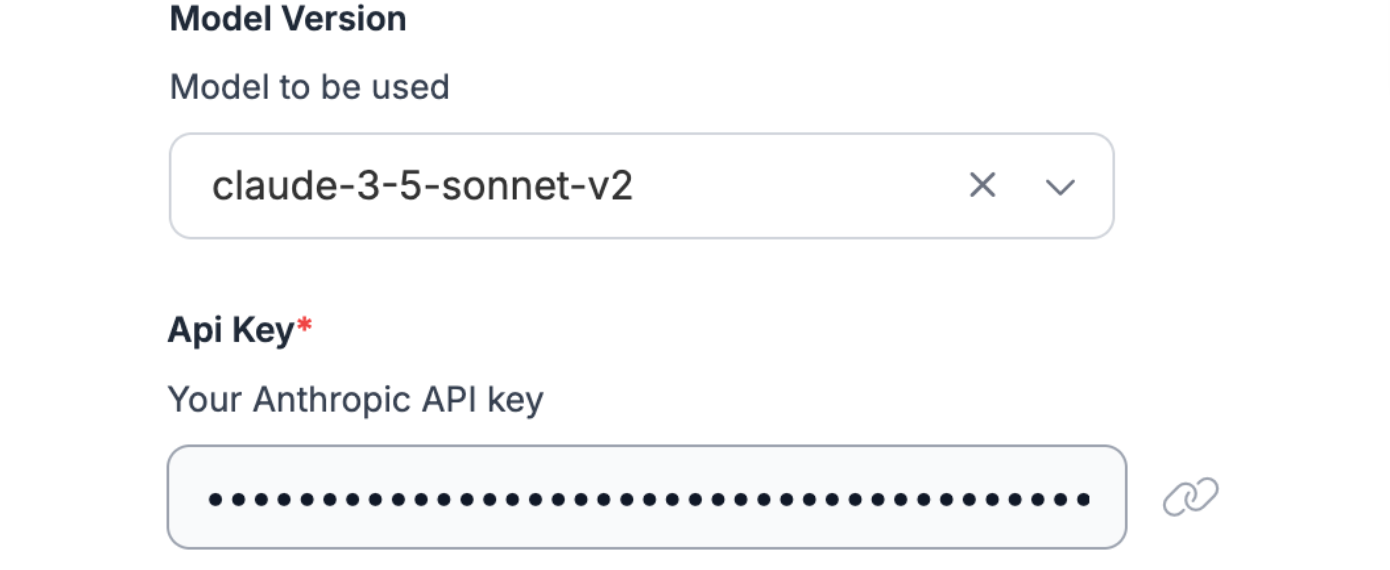
Next, we’ll actually have to fine-tune 3.7 Sonnet to give us structured JSON responses/visual question answering on the fruit images.
In the Anthropic block settings, change the task type to Structured Output Generation:
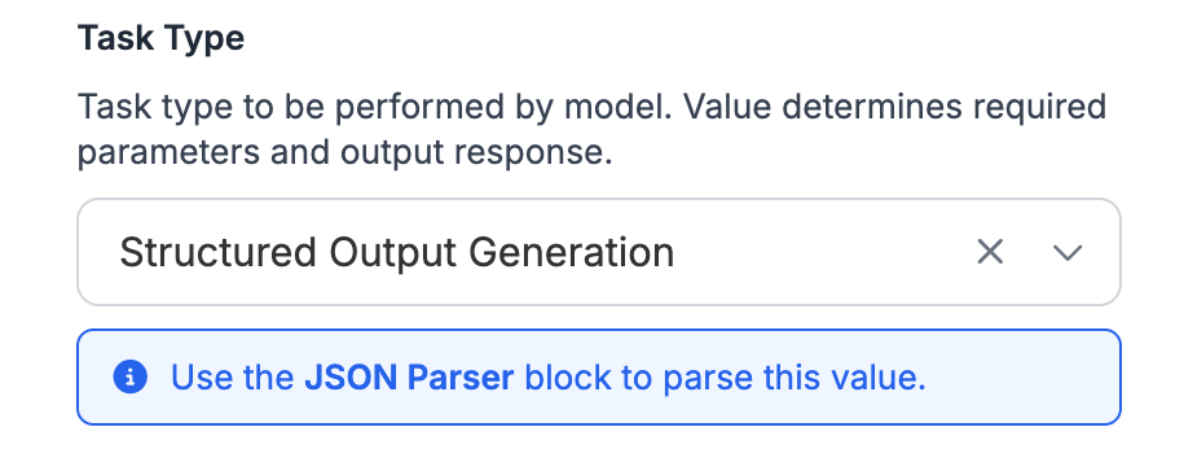
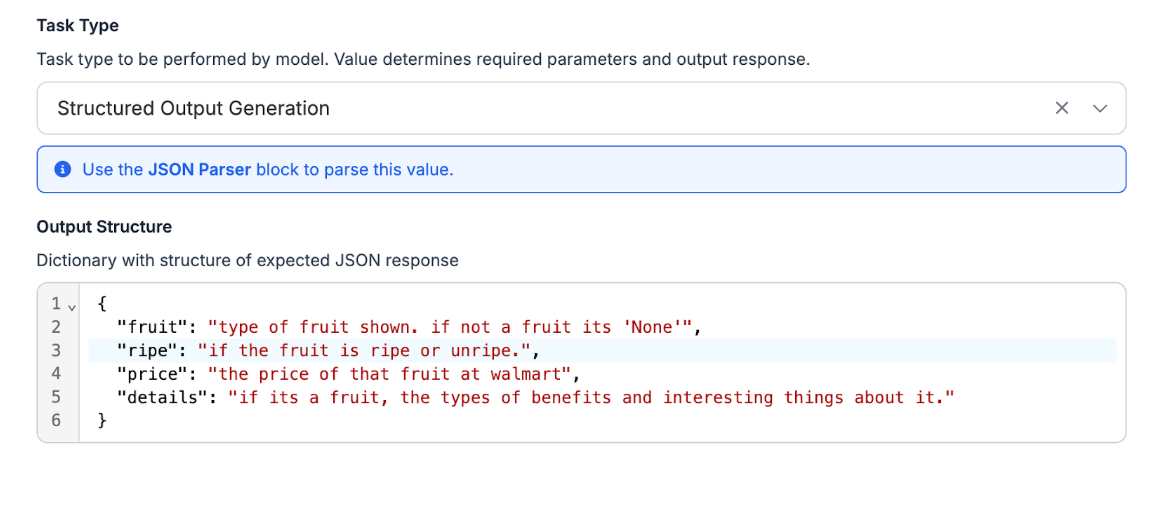
The last step is to provide a JSON with the results we want from the model. Here's an example of the details we’d want Claude to be able to provide from an image of fruit:
{
"fruit": "type of fruit shown. if not a fruit its 'None'",
"ripe": "if the fruit is ripe or unripe.",
"price": "the price of that fruit at walmart",
"details": "if it’s a fruit, the types of benefits and interesting things about it."
}
Now, we’ll add this to the Output Structure in the block settings:
Next, to be able to use these results effectively, we need to add a JSON Parser block to the workflow, that will give a formatted JSON/dictionary of the values we wanted:
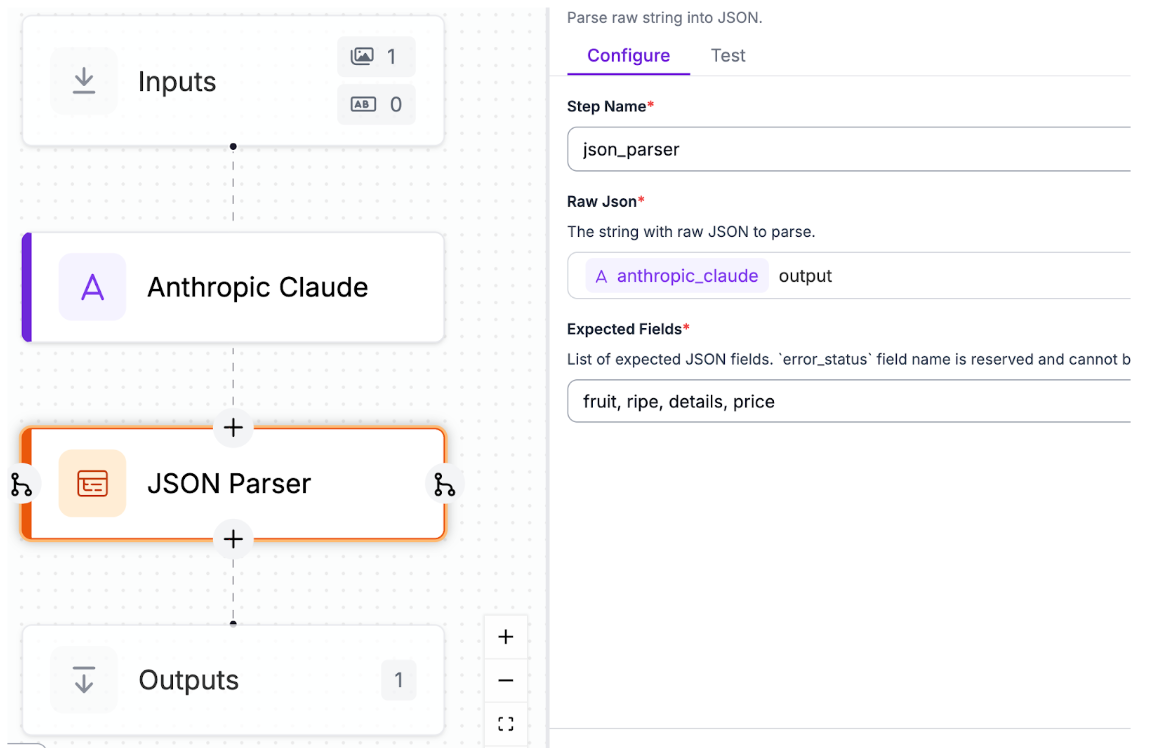
Here, we’ve set the expected fields option to the values that we provided earlier.
And with that, the workflow is complete!
Testing the Workflow
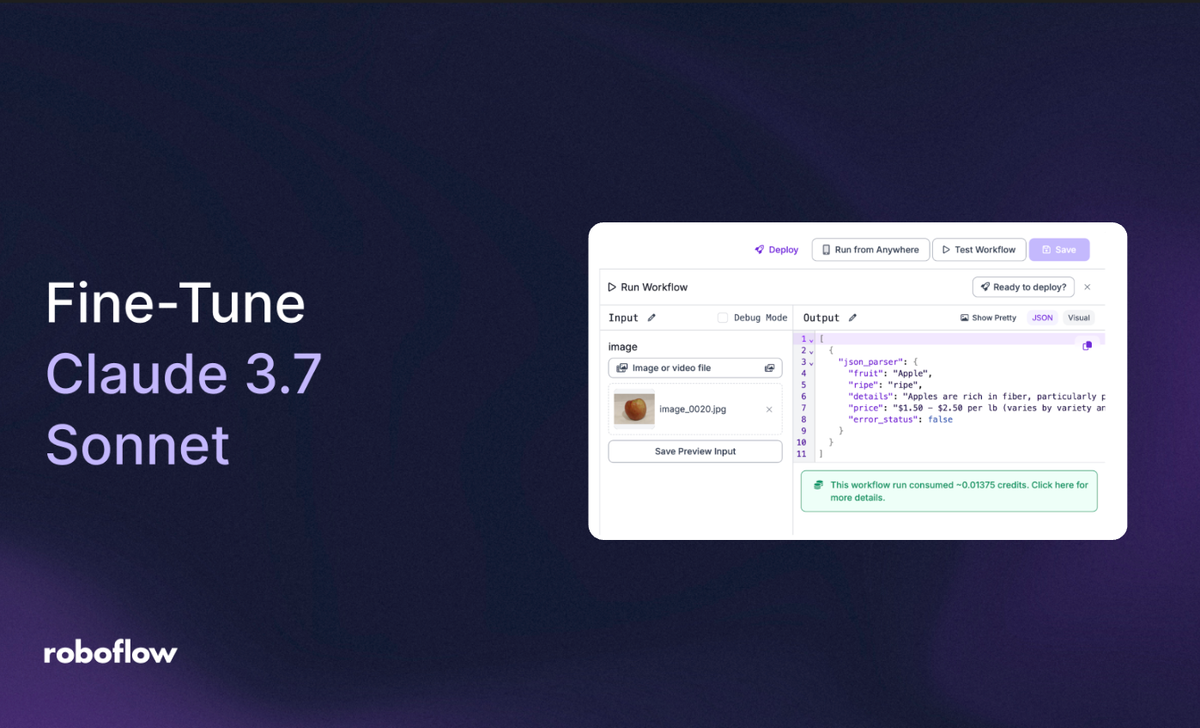
Before deploying, it’s beneficial to test the workflow on images so that we can be sure that there’s no errors and we’re getting exactly what we expected. Heading over to the testing tab in the workflow, you can upload an image of fruit and examine the outputs:
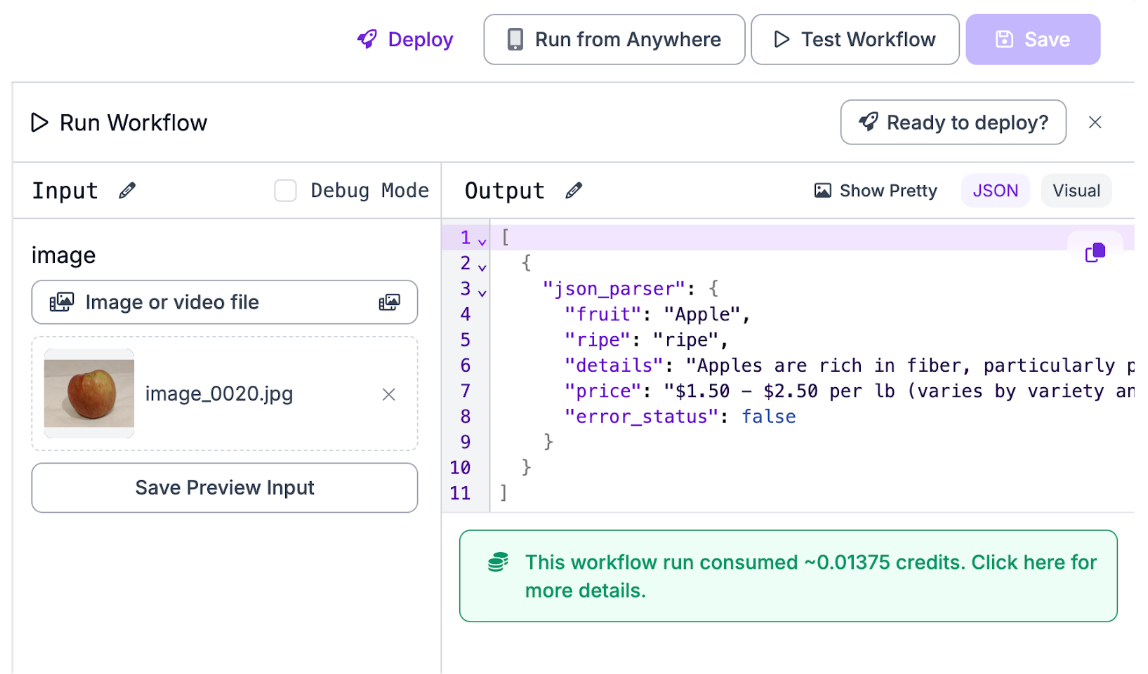
Output:
[
{
"json_parser": {
"fruit": "Apple",
"ripe": "ripe",
"details": "Apples are rich in fiber, particularly pectin, which supports digestive health. They contain vitamin C and various antioxidants, including quercetin and catechin. Regular apple consumption is associated with reduced risk of heart disease, improved lung function, and better weight management. The phrase 'an apple a day keeps the doctor away' reflects their health benefits. Apples are one of the most widely cultivated fruits globally, with over 7,500 varieties. They're versatile for eating fresh, cooking, baking, and making cider.",
"price": "$1.50 - $2.50 per lb (varies by variety and season)",
"error_status": false
}
}
]With this, we can see that the workflow is working properly. Additionally, all of the outputs that we need are stored in “json_parser”, which will be helpful for when we wish to deploy the program.
Deploy
To deploy the workflow, Roboflow provides a helpful, low-code solution, for running the workflow on images, which is what we’ll be using. Head over to the deploy tab, and follow the steps to get the deployment code and instructions:
From here, create a file called main.py, and add the code:
from inference_sdk import InferenceHTTPClient
client = InferenceHTTPClient(
api_url="https://serverless.roboflow.com",
api_key="Fn4IR0RSauo7xH4alhjC"
)
result = client.run_workflow(
workspace_name="personal-ky365",
workflow_id="custom-workflow",
images={
"image": "YOUR_IMAGE.jpg" # Path to your image file
},
use_cache=True # Speeds up repeated requests
)
print(result)To be able to use this code, you’ll have to install the inference-sdk library in python. In the terminal, run:
pip install inference-sdk
Finally, add an image inside the same directory as main.py, and replace the image path in the code with the image path of the new image:

result = client.run_workflow(
workspace_name="personal-ky365",
workflow_id="custom-workflow",
images={
"image": "fruit.jpg" # Path to your image file
},
use_cache=True # Speeds up repeated requests
)Finally, running the program:
[{'json_parser': {'fruit': 'Dragon fruit (Pitaya)', 'ripe': 'ripe', 'details': "Dragon fruit is rich in antioxidants, vitamin C, and fiber. It supports immune function, aids digestion, and promotes healthy skin. The fruit is low in calories (about 60 calories per 100g) and contains prebiotics that support gut health. It has a mildly sweet taste and can be eaten fresh or added to smoothies. The black seeds are edible and contain omega-3 and omega-9 fatty acids. Dragon fruit may help regulate blood sugar levels and has anti-inflammatory properties. It's also high in iron and magnesium.", 'price': '$4.98 - $6.98 per fruit (prices vary by location and season)', 'error_status': False}}]
Fine-Tuned Claude 3.7 Sonnet Conclusion
And there you have it! In just a few steps, we've fine-tuned Claude 3.7 Sonnet to analyze fruit images and return structured JSON outputs, but this same workflow can be adapted for manufacturing defect detection, medical imaging, retail analytics, or any domain requiring reliable visual analysis. The combination of Claude's advanced multimodal reasoning with Roboflow's intuitive workflow builder gives you production-ready, structured data that integrates seamlessly into your applications.
Written by Aryan Vasudevan
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Contributing Writer. (Dec 10, 2025). How to Fine-Tune Claude 3.7 Sonnet With Roboflow. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/fine-tune-claude-3-7-sonnet/
