
Computer vision used to require deep machine learning expertise and countless hours of coding. Today, no-code platforms have democratized vision AI, making it accessible to anyone, regardless of technical background. It doesn’t matter if you're building a rust detection system, counting objects in images, or automating visual inspection; you don't need to write a single line of code.
This guide covers the most powerful no-code and low-code computer vision platforms available, explaining what each excels at, who should use them, and how they compare.
Explore the Best No-Code Computer Vision Tools
1. Roboflow
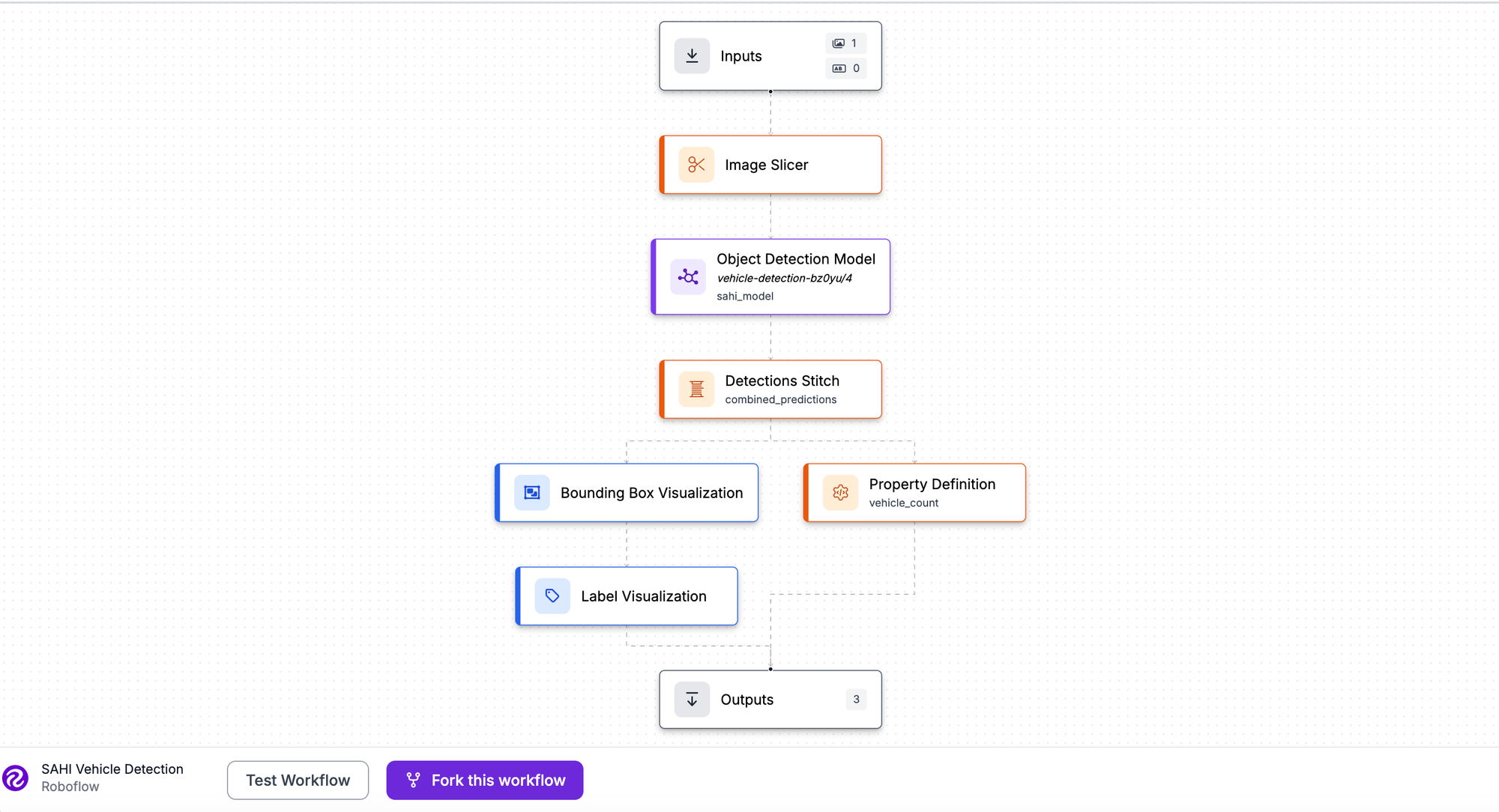
Roboflow is an end-to-end computer vision platform designed for teams building production-ready models. It combines dataset management, annotation, model training, and deployment into a single intuitive interface. From labeling raw images to deploying models at the edge, Roboflow handles the entire lifecycle.
Best for: Teams of all sizes building custom vision applications; enterprises needing scalable ML infrastructure; anyone wanting a true end-to-end platform with multi-task support.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Complete end-to-end workflow: annotation, training, and robust deployment (cloud, edge, on-premise) | Steeper learning curve than single-task tools |
| AI-assisted labelling with Auto Label and the integrated Segment Anything Model (SAM) | Paid plans are required for advanced enterprise features and high usage limits |
| Supports 10+ vision tasks (classification, detection, segmentation, key point detection, OCR) | |
| Built-in preprocessing, augmentation, and dataset health checks | |
| Pre-built Workflows combining multiple models for complex pipelines | |
| Excellent edge deployment and mobile integration (e.g., dedicated iOS/Android SDKs) | |
| Comprehensive API and SDK support for all major languages/frameworks |
Follow this tutorial to get started with Roboflow.
2. Google Vertex AI Vision
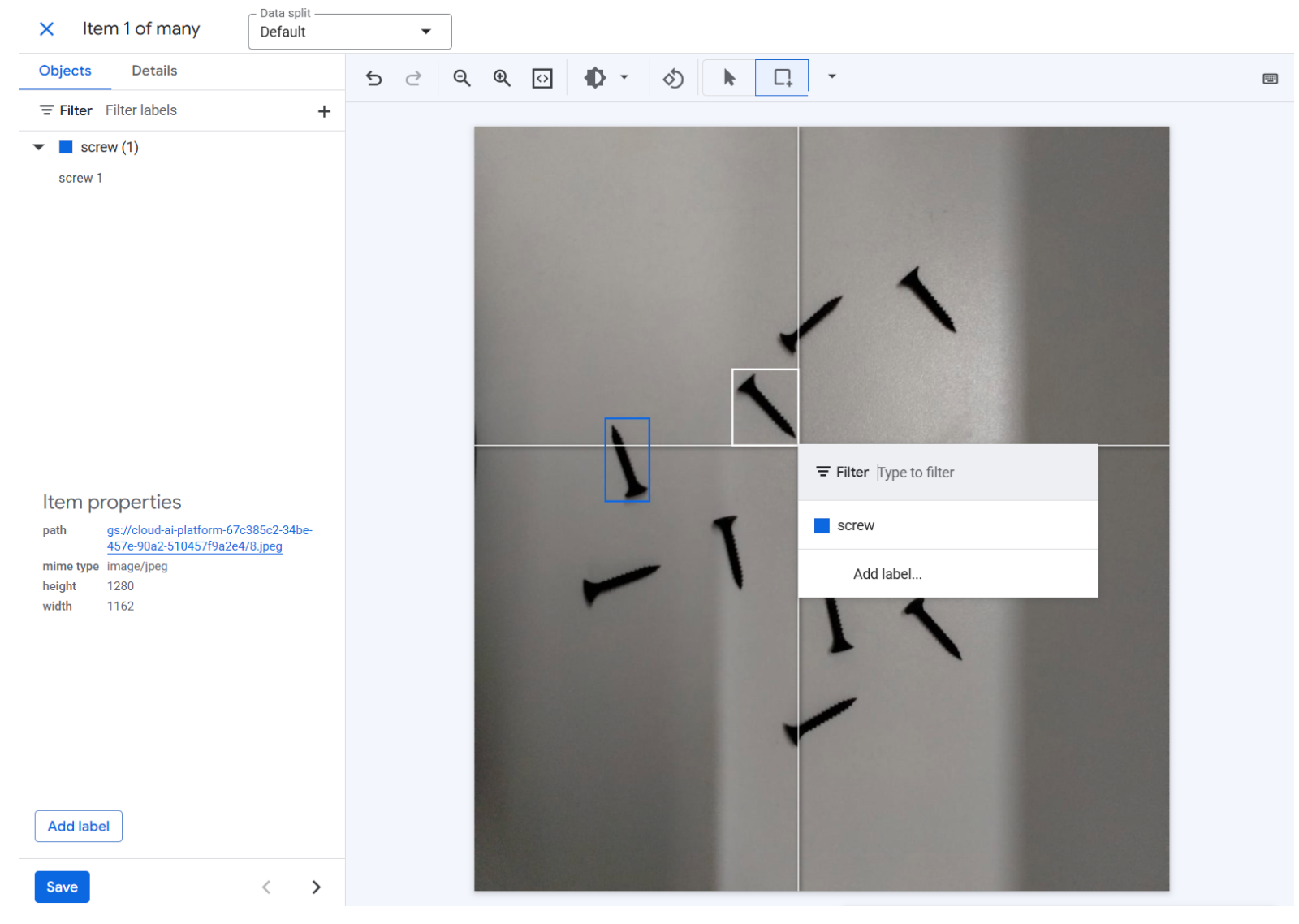
Google AutoML Vision has been fully integrated into Google Cloud's Vertex AI platform. It is Google's managed machine learning service for custom vision models. Hosted entirely on Google Cloud, it handles vision tasks through a streamlined web interface. Google manages the infrastructure and computational resources, making it ideal for enterprises with large datasets already leveraging the Google Cloud ecosystem.
Best for: Enterprises; teams already committed to Google Cloud; projects requiring enterprise-grade SLA support and robust integration with other Vertex AI/GCP services; large-scale, high-data-volume projects.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| No infrastructure management required (fully managed service) | High cost for training and inference compared to other platforms |
| Handles extremely large datasets efficiently and at scale | Requires a Google Cloud account and payment method |
| Built-in data labeling service with managed workforce options | Requires an internet connection for training and deployment |
| Automatic model optimization for accuracy and performance | It can be slower for rapid prototyping due to its enterprise focus |
| Deep integration with Google Cloud monitoring, security, and data services |
Here’s a beginner's guide to Google’s Vertex AI vision from AutoML.
3. Create ML
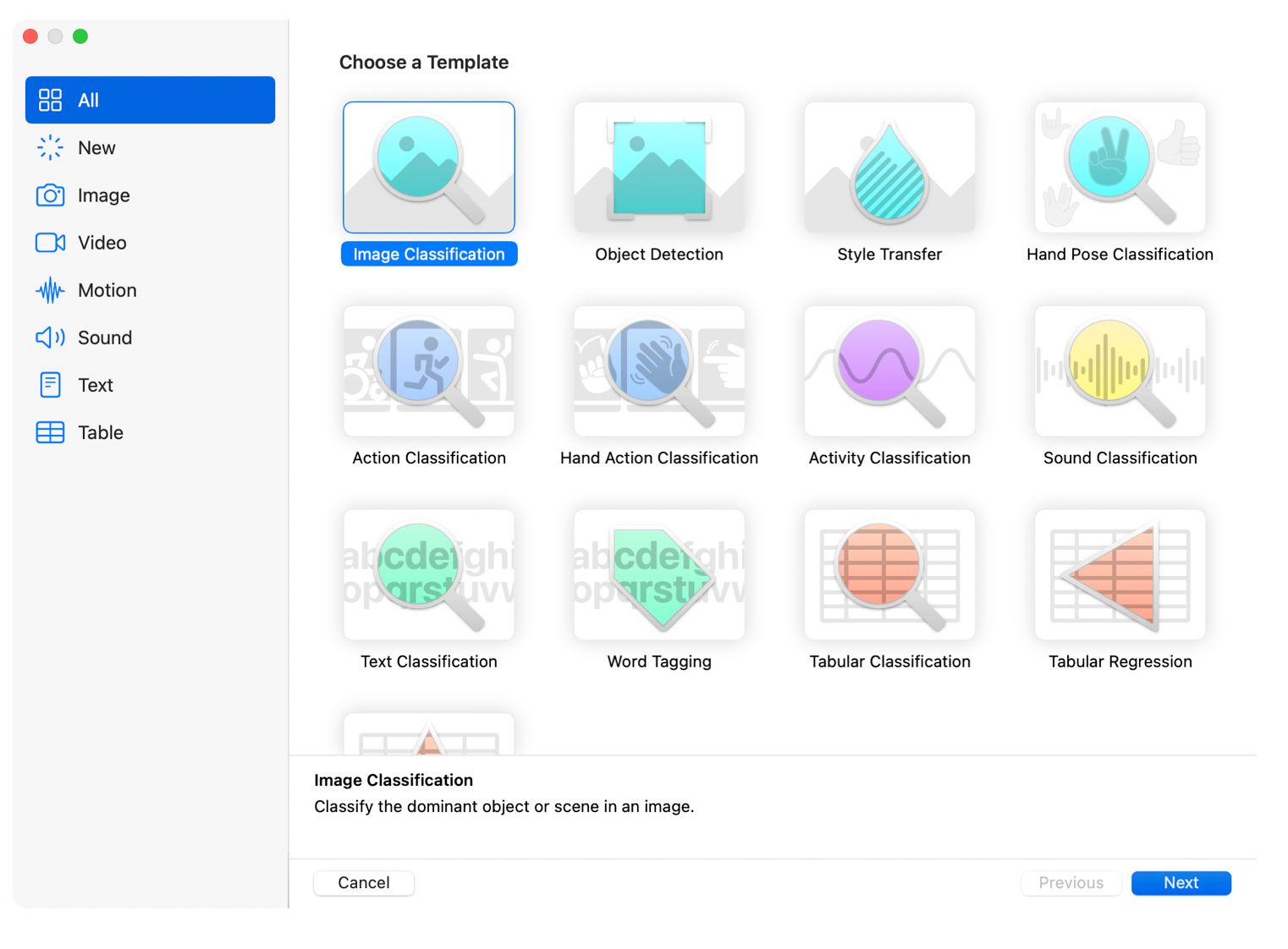
Create ML is Apple's native machine learning tool for macOS, iOS, and other Apple platforms. Integrated into Xcode, it lets developers train models directly on their Mac and deploy them seamlessly to iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches.
Best for: Apple developers; iOS/macOS app developers; teams building on-device ML features; privacy-focused apps requiring edge inference on Apple hardware.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Integrated into Xcode and the macOS ecosystem | Mac/Xcode required to train models |
| On-device inference (Core ML format) is fast and privacy-focused | Models deploy only to Apple devices |
| Supports multiple vision tasks: classification, object detection, style transfer, action classification, and segmentation (via different models) | Limited to Apple's supported model architectures |
| Fast training with Apple Silicon acceleration (M1, M2, M3, etc.) | Requires understanding of Apple development tools |
| Free (included with Xcode) |
Follow this proper guide for CreateML.
4. Mediapipe
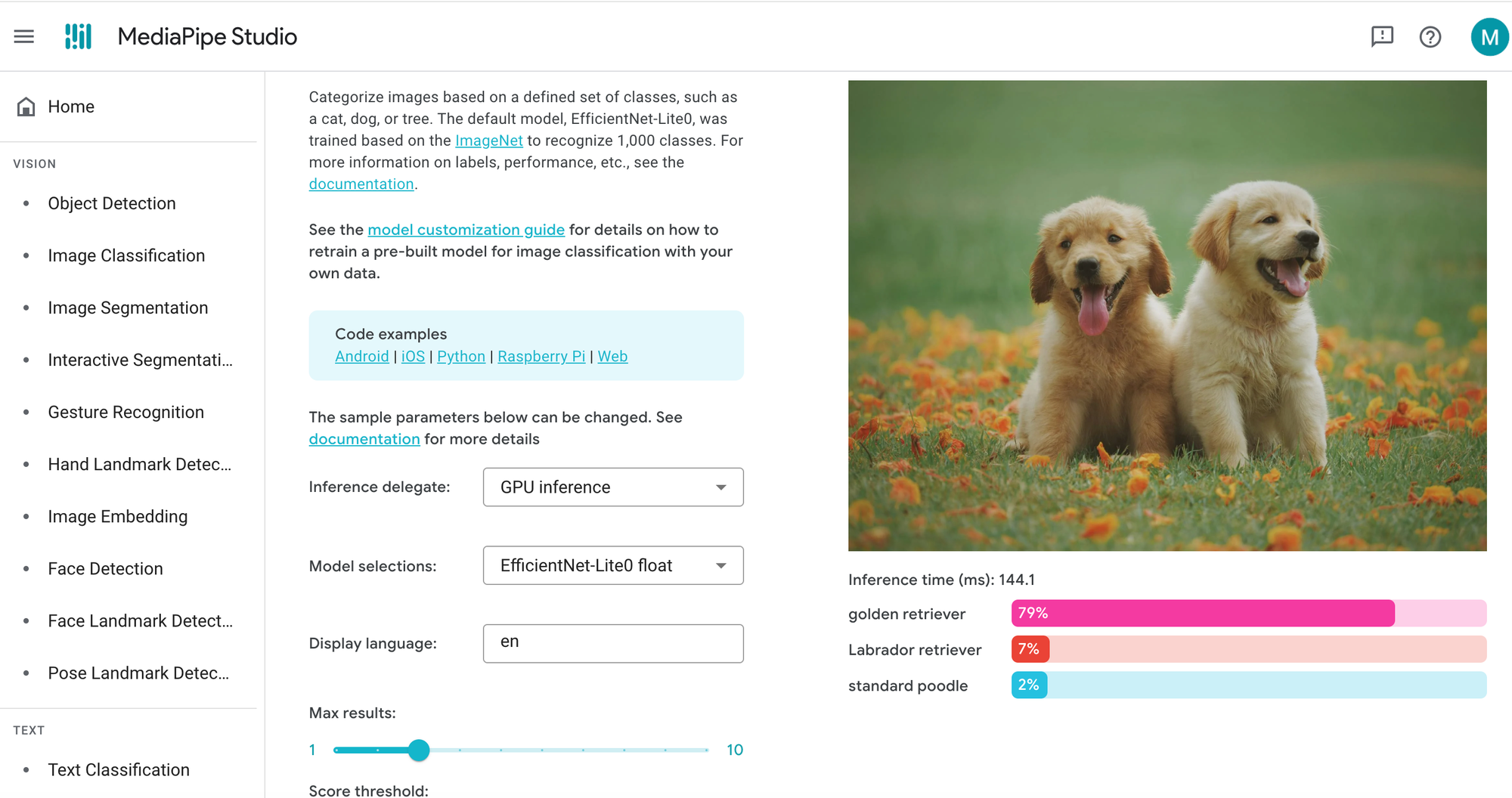
MediaPipe, developed by Google, is an open-source framework offering ready-to-use solutions for real-time computer vision tasks. Instead of training from scratch, you integrate pre-built, optimized models for tasks like hand tracking, pose estimation, face detection, and object detection. It is a low-code solution, as integration typically requires writing code.
Best for: Developers needing quick, high-performance solutions; real-time applications (video, AR/VR); gesture and pose tracking; projects where pre-built models suffice; cross-platform development.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Free and open-source | Requires code to integrate (not truly no-code) |
| Pre-built, optimized models ready to use immediately | Limited to pre-built models (custom training is not a core feature) |
| Excellent performance on mobile and edge devices | Not ideal for specialized domains requiring custom training |
| Supports a wide range of tasks optimized for human interaction (pose, hands, face) | No native, built-in OCR or full text recognition |
| Low latency; designed for real-time inference |
For more information on how to use Mediapipe, use Roboflow’s beginner-friendly Mediapipe tutorial.
5. Intel Geti
Intel Geti is an end-to-end computer vision platform emphasizing speed, data efficiency, and collaboration, particularly for industrial and enterprise use cases. It enables teams to build custom models with minimal data through Active Learning, smart annotations, and automatic model optimization.
Best for: Teams collaborating on vision projects; industrial applications (e.g., manufacturing quality control); anyone needing to train with minimal data and leverage Active Learning; autonomous systems.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Active Learning: model guides labeling by identifying the most valuable samples, minimizing manual effort | Focuses heavily on the enterprise/industrial market (less for hobbyists) |
| Requires minimal training data (often less than 50 samples to start) | Requires learning the platform's specific workflow |
| Smart annotations reduce manual labelling effort significantly | No free tier |
| Team collaboration features built-in | |
| Optimized for edge deployment with OpenVINO | |
| Supports object detection, classification, and segmentation |
See video tutorials on how Intel Geti is used here.
6. OpenAI AgentKit
OpenAI's AgentKit includes the Agent Builder, a visual workflow platform for creating multi-step AI agents. While it won't train an object detection model like Roboflow, it excels at using powerful multimodal models like GPT-4o or GPT-5 for real-time analysis, acting as an orchestration layer that combines vision with language, logic, and external actions. It's essentially the "Zapier for AI Agents," where vision analysis is a block in a larger automation flow.
Best for: Developers and enterprises building multimodal agents; complex automation workflows combining vision with language and external API calls (e.g., "Visual Triage"); anyone needing to integrate an LLM's reasoning with image analysis.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Visual, drag-and-drop workflow design (Agent Builder) | No native dataset management or custom model training (must use external APIs/tools) |
| Seamlessly integrates GPT-4o/GPT-5 vision for image analysis | Vision capability is limited to what the LLM can interpret (not specialized detection or segmentation training) |
| SConnects vision output to external tools/APIs (e.g., read a receipt image, then post the structured data to a database) | Overkill for simple, single-task vision problems (e.g., pure classification) |
| Includes deployment tools (ChatKit) and governance features (Guardrails) | Requires code or a custom MCP (Manifests for Custom Plugins/Tools) to integrate highly specialized external vision models |
| Ideal for Visual Triage use cases (e.g., agent sees an error screen, reasons about it, and then files a ticket) | Learning curve for multi-step agent design and tool creation |
How it works: In the Agent Builder's visual canvas, you can define an agent workflow that starts with a user uploading an image. A node in the workflow uses the model's vision capability to analyze the image (e.g., "describe the state of the machine" or "extract text from this document"). The agent then uses its reasoning to decide the next step, such as routing the description to a human-in-the-loop for approval or automatically calling an external API to update an inventory count.
Feature Comparison Matrix
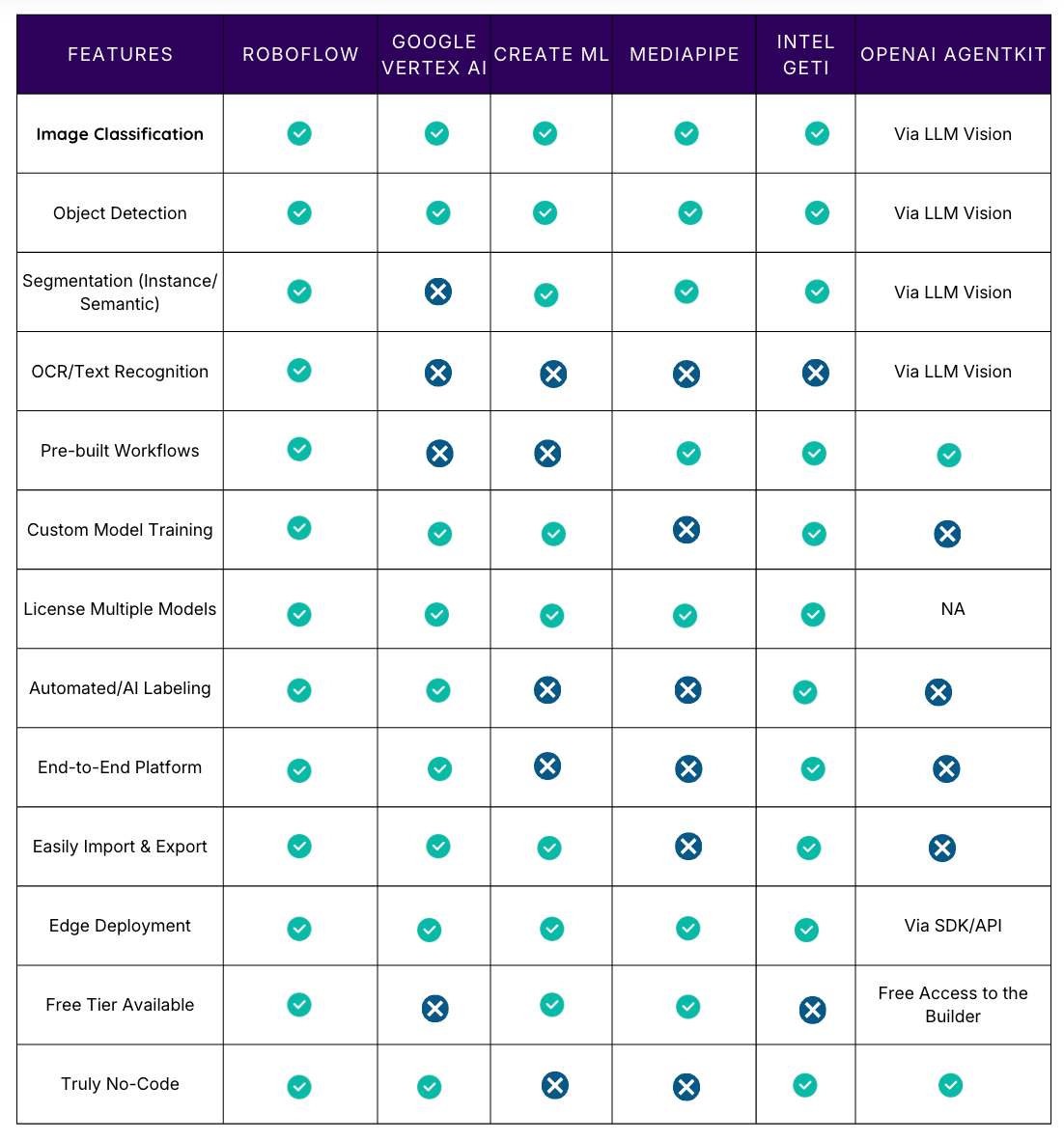
How to Choose the Right No-Code Computer Vision Platform
- Choose Roboflow if: You require an end-to-end platform, require multiple vision tasks (detection, segmentation, OCR), want to deploy at scale, or need the best AI-assisted labelling tools. It is the most versatile option for production systems.
- Pick Google Vertex AI Vision if: Your team is already deeply invested in Google Cloud, you have massive budgets, need enterprise support, or have large datasets (1,000+ images).
- Go with Create ML if: You're building iOS/macOS apps and want models to run natively on Apple devices. It integrates seamlessly into Apple's development ecosystem.
- Select MediaPipe if: You require pre-built solutions for real-time, human-centric tasks (pose, hands, face) and are comfortable integrating a low-code framework into an existing application.
- Use Intel Geti if: You are in an industrial setting, have limited training data, and require advanced active learning and collaborative annotation assistance.
- Use OpenAI AgentKit if: You need to build a complex, multimodal workflow that connects image analysis (via LLM Vision or external tools) to business logic, reasoning, and external actions (e.g., automatically filing a ticket after an agent visually confirms a manufacturing defect).
Get Started with The Best No-Code Computer Vision Platforms
The barrier to building computer vision applications has never been lower. Upload your images to Roboflow, and start building today. No coding required.
Written by Aarnav Shah
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Contributing Writer. (Dec 1, 2025). No-Code Computer Vision Tools & Platforms: Beginner's Guide. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/no-code-computer-vision-tools/
