
RF-DETR-Seg is a real-time transformer architecture for instance segmentation developed as an extension of RF-DETR detection. The model adds a segmentation head on top of the existing detection pipeline while preserving the same real-time inference characteristics.
Video 1. RF-DETR-Seg running instance segmentation in real time.
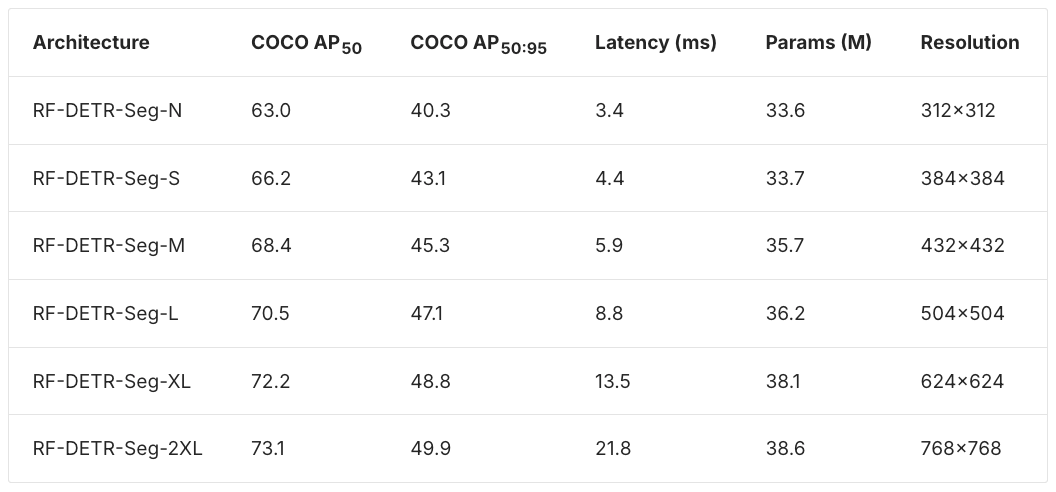
This release introduces pre-trained RF-DETR-Seg checkpoints across the full model scale, from Nano to 2XLarge. All RF-DETR-Seg checkpoints released in this update are available under the Apache 2.0 license and ship with RF-DETR version 1.4 and later.
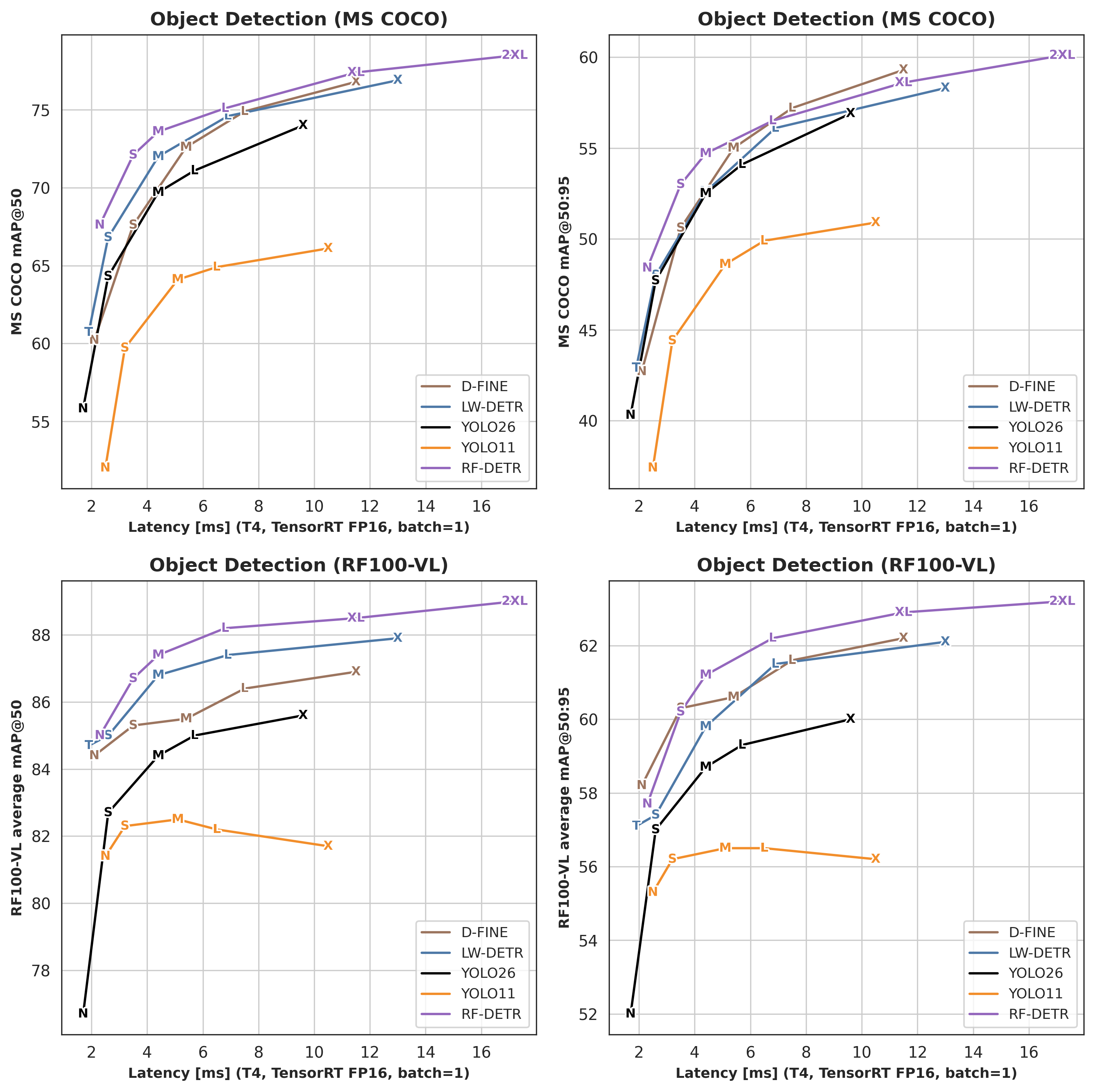
Alongside segmentation, this release also publishes new object detection checkpoints for Large, XLarge, and 2XLarge. The XLarge and 2XLarge detection models are based on DINOv3 and are released under the Platform Model License 1.0.
Performance
Across all model sizes, RF-DETR-Seg outperforms other real-time instance segmentation models in accuracy while maintaining competitive latency. In particular, RF-DETR-Seg exceeds the performance of YOLO26 segmentation models released last week.
The released checkpoints differ in both model capacity and input resolution. Smaller models target lower latency at reduced resolution, while larger models trade higher resolution and parameter count for improved mask quality.
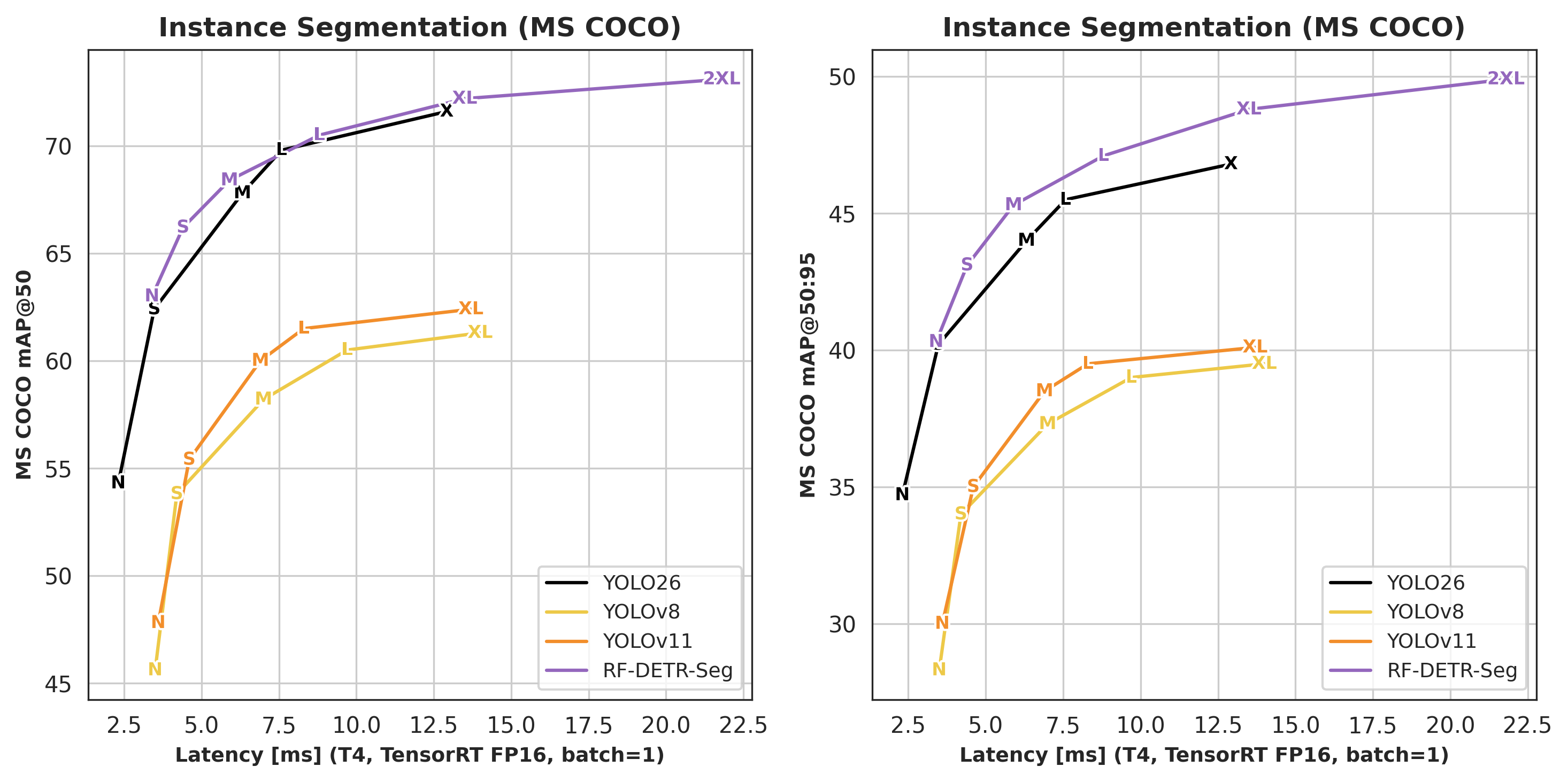
Instance segmentation benchmarks are reported on Microsoft COCO using standard AP50 and AP50:95 metrics. Latency measurements reflect single-image inference on an NVIDIA T4 using TensorRT with FP16 precision and batch size one.
Run RF-DETR Segmentation Model
The examples below show how to run instance segmentation using the RF-DETR Python package and using Roboflow Inference. Both options expose the same pre-trained RF-DETR-Seg checkpoints and target different deployment scenarios.
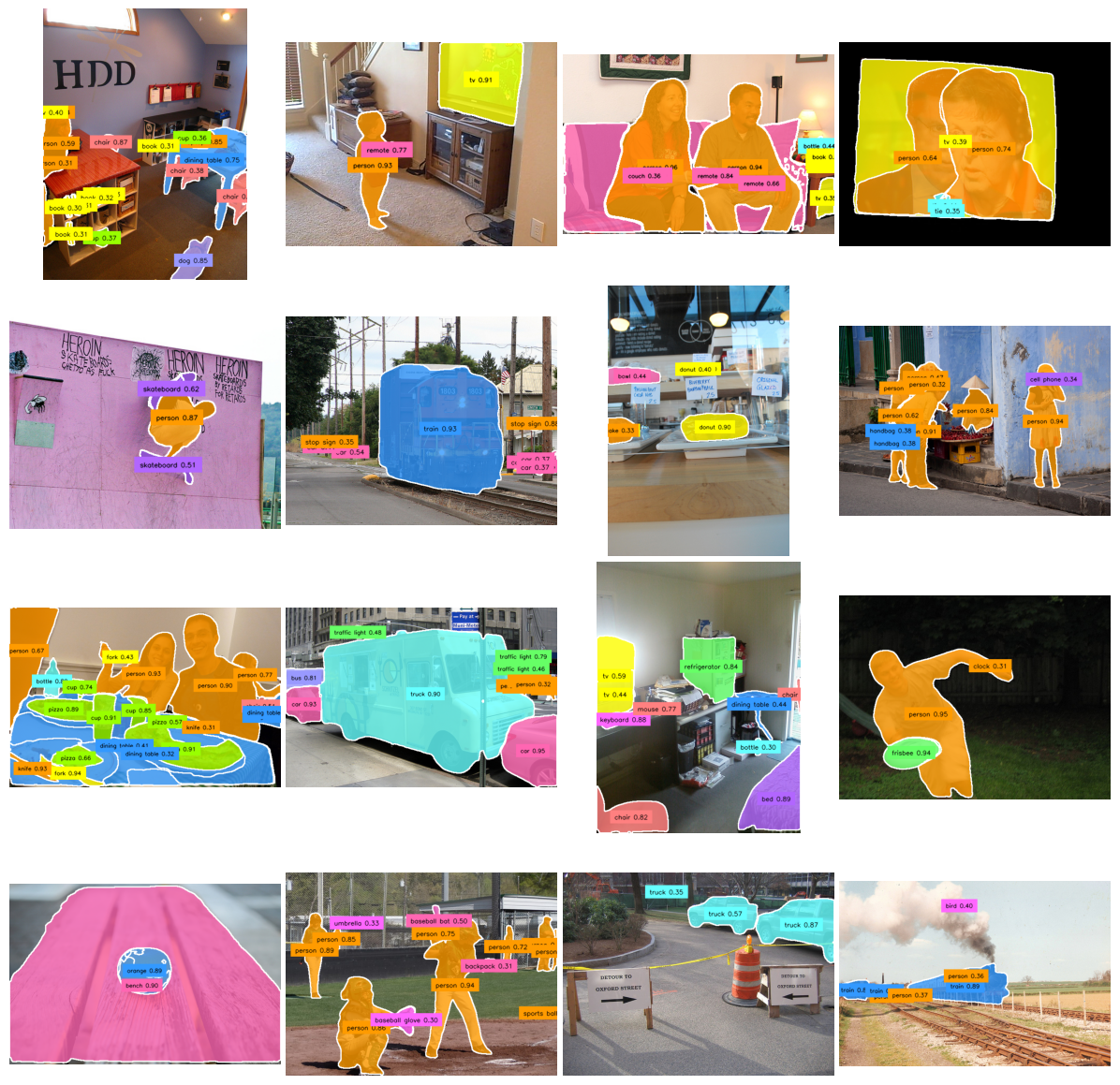

When running inference, you should select a model size that matches your accuracy and latency requirements. Smaller models prioritize inference speed, while larger models prioritize segmentation accuracy.
When switching model sizes in the RF-DETR package, select the corresponding class such as RFDETRSegNano, RFDETRSegSmall, or RFDETRSegMedium. When running inference through Roboflow Inference, select the matching model alias for the desired checkpoint such as rfdetr-seg-nano, rfdetr-seg-small, or rfdetr-seg-medium.
import requests
import supervision as sv
from PIL import Image
from rfdetr import RFDETRSegMedium
from rfdetr.util.coco_classes import COCO_CLASSES
model = RFDETRSegMedium()
image = Image.open(requests.get('https://media.roboflow.com/dog.jpg', stream=True).raw)
detections = model.predict(image, threshold=0.5)
labels = [
f"{COCO_CLASSES[class_id]}"
for class_id
in detections.class_id
]
annotated_image = sv.MaskAnnotator().annotate(image, detections)
annotated_image = sv.LabelAnnotator().annotate(
annotated_image, detections, labels)
Running RF-DETR-Seg inference with the open-source RF-DETR Python package.
import requests
import supervision as sv
from PIL import Image
from inference import get_model
model = get_model("rfdetr-seg-medium")
image = Image.open(requests.get('https://media.roboflow.com/dog.jpg', stream=True).raw)
predictions = model.infer(image, confidence=0.5)[0]
detections = sv.Detections.from_inference(predictions)
annotated_image = sv.MaskAnnotator().annotate(image, detections)
annotated_image = sv.LabelAnnotator().annotate(
annotated_image, detections)Running RF-DETR-Seg inference with the open-source Inference Python package.
Fine-Tune RF-DETR Segmentation Model
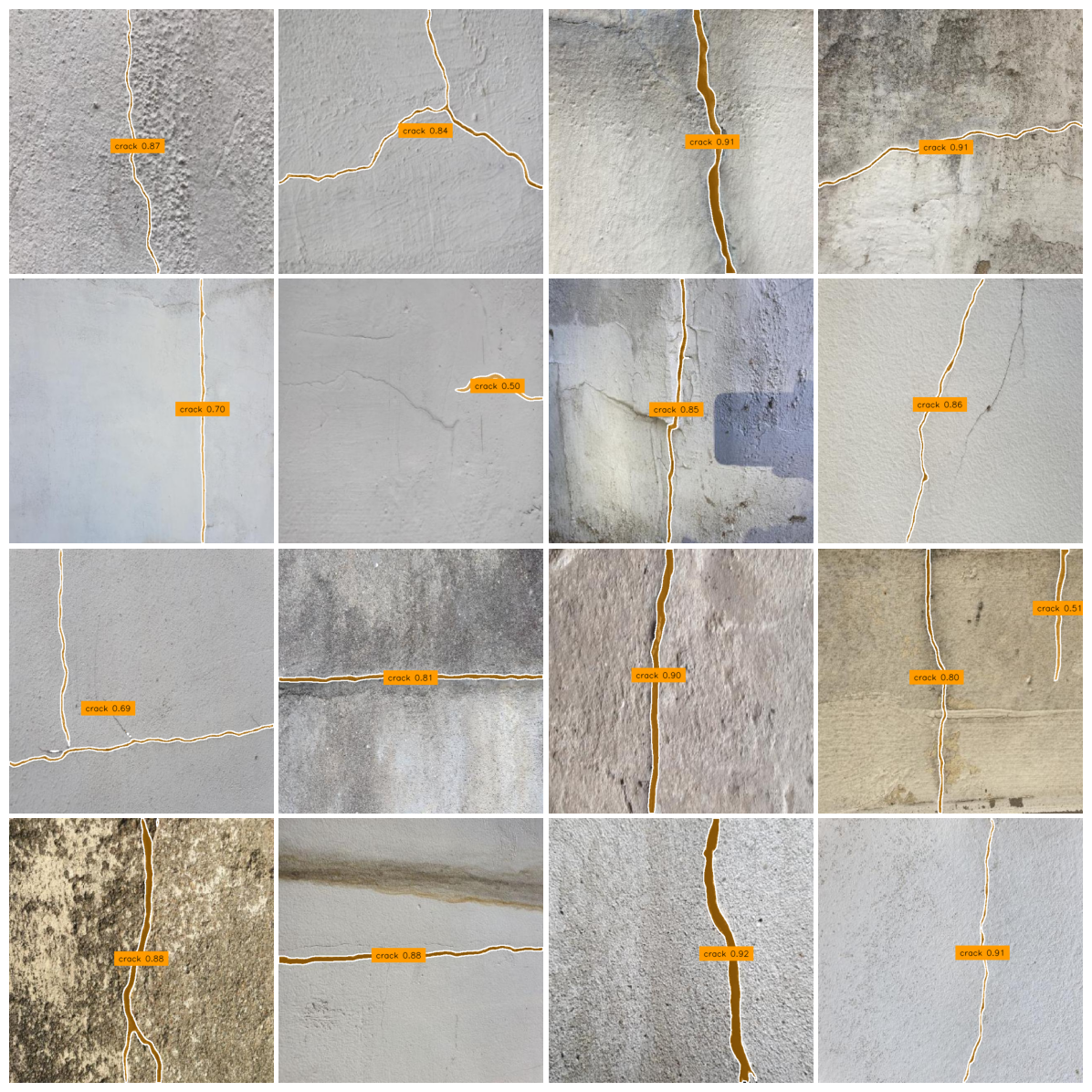
RF-DETR-Seg supports fine-tuning through the open-source RF-DETR Python package. Training starts from the pre-trained segmentation checkpoints released in this update and targets custom instance segmentation datasets.
Check out how to fine-tune RF-DETR-Seg on a custom segmentation dataset.
Training requires a labeled dataset. Datasets must follow either COCO or YOLO instance segmentation format, which RF-DETR detects automatically based on directory structure.
If you do not already have a dataset, Roboflow Universe provides a large collection of labeled datasets suitable for instance segmentation.

from rfdetr import RFDETRSegMedium
model = RFDETRSegMedium()
model.train(
dataset_dir=<DATASET_PATH>,
epochs=100,
batch_size=4,
grad_accum_steps=4,
lr=1e-4,
output_dir=<OUTPUT_PATH>
)
RF-DETR exposes a range of training parameters such as learning rate, batch size, gradient accumulation, checkpointing behavior, and logging. These options support adaptation to different hardware setups and dataset sizes without changing the training workflow. Full parameter descriptions are available in the RF-DETR documentation.
RF-DETR-Seg models can also be trained directly on the Roboflow Platform. The platform handles data loading, checkpointing, and hardware configuration without changing the underlying model behavior.
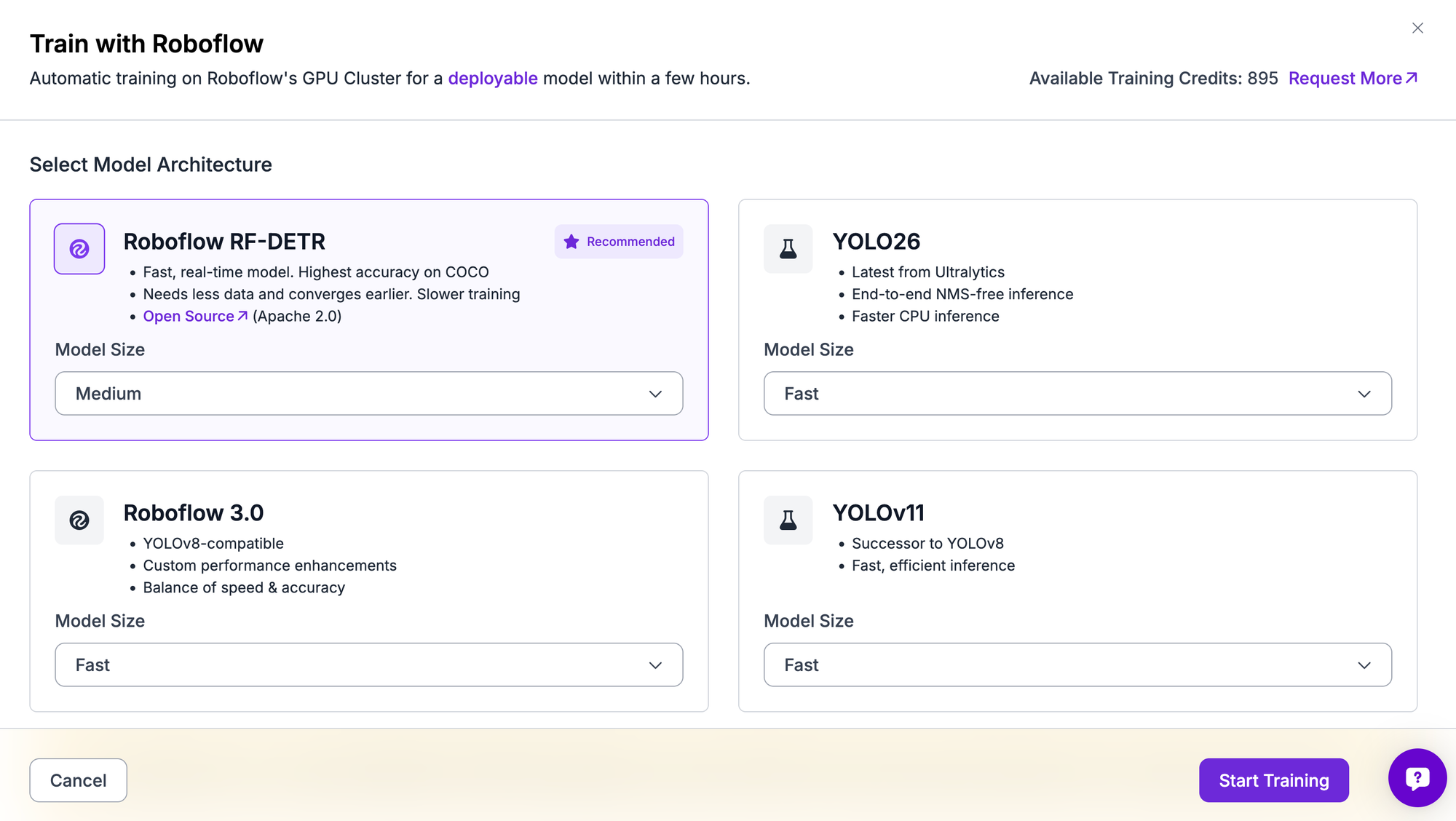
To train a model, you select RF-DETR Segmentation as the architecture and choose a model size that matches your accuracy and latency requirements. Training runs from a pretrained checkpoint by default, which shortens convergence time and improves final mask quality. Training duration depends primarily on dataset size and selected model scale.
Summary
RF-DETR first reached state-of-the-art results in object detection, outperforming widely used models such as YOLO. With this release, RF-DETR-Seg reaches the same level for real-time instance segmentation, offering strong accuracy across a wide range of model sizes while keeping inference latency practical.
Development on RF-DETR continues. Stay tuned for future releases in the RF-DETR repository, as we actively expand support for additional computer vision tasks.
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Piotr Skalski. (Jan 22, 2026). New RF-DETR Segmentation Checkpoints from Nano to 2XLarge. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/rf-detr-segmentation/
