
Whether you practice sports for your health and fitness or you’re a professional athlete, sports bring people together. Having been around for so long, sports have also seen many technological advancements over the years.
Recently, computer vision, the technology that enables computers to analyze and interpret visual data from the real world, has gained popularity for sports analysis and analytics.
Computer vision in sports opens up a wide variety of new tools for teams, coaches, sports analytics professionals, scouts, as well as fans. It can be used to build capabilities like real-time video analysis, fitness and health tracking, and sports predictions, and enhancing the overall fan experience. In this article, we’ll dive into various use cases of computer vision in sports and its applications.
Key Applications of Computer Vision in Sports
With the global sports market expected to reach around $6.69 billion in 2028, many companies and sports organizations are looking into investing in and adopting AI and computer vision tools. Let’s take a look at some of the key applications of computer vision in sports.
Player and Ball Tracking
Computer vision in player and ball tracking has become a very powerful tool in sports analysis. By accurately detecting and tracking the movements of players and the ball, analysts can gain valuable insights into the performance of the players, team strategies, and game dynamics.
Whether it's football, basketball, or cricket, such tracking systems can be used to record precise 3D trajectories, predict ball paths, and even identify player interactions. Computer vision helps the fans better understand the game, aids players in refining their skills, and helps coaches develop effective strategies.
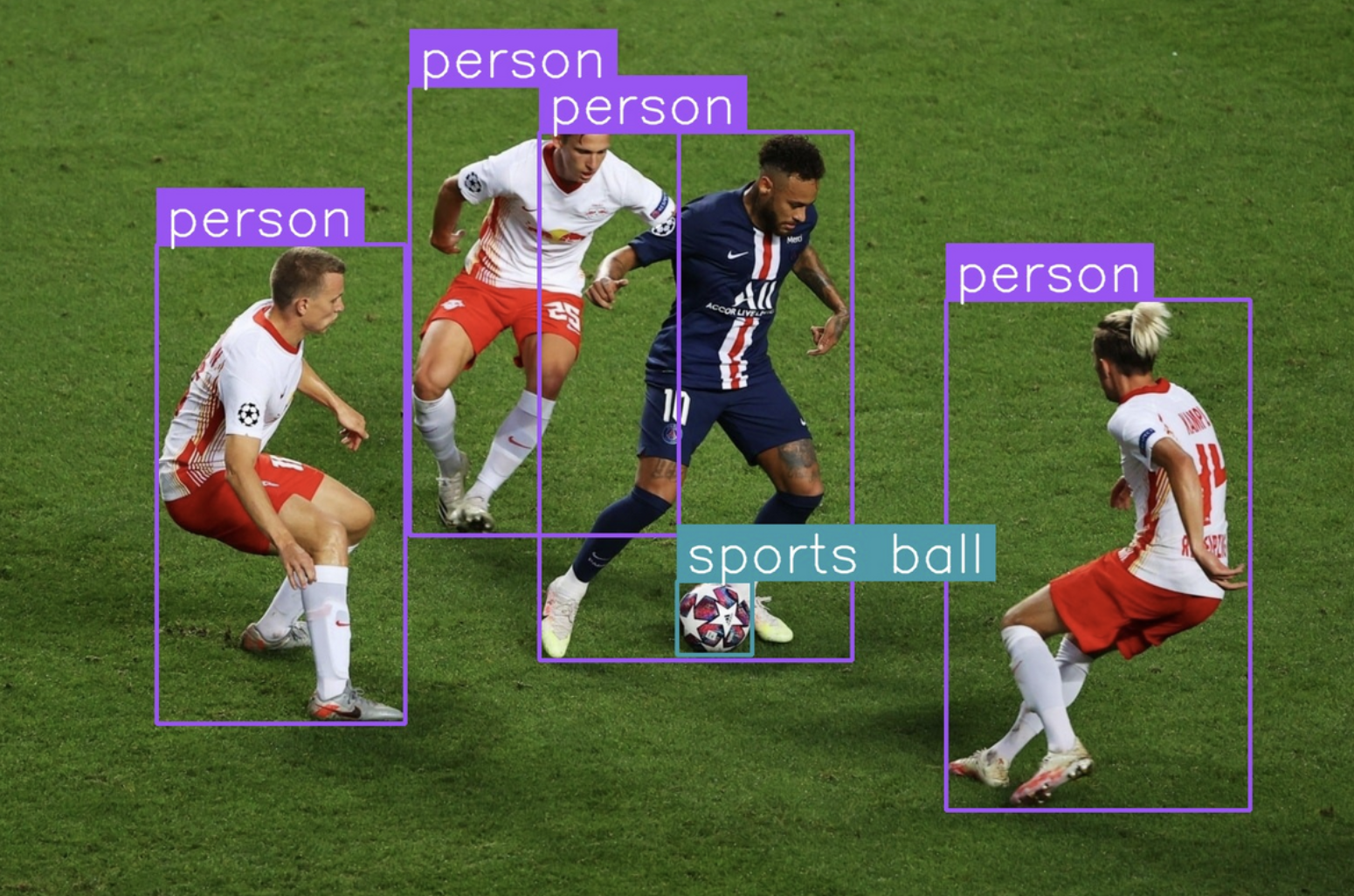
Referee Assistance and VAR (Video Assistant Referee)
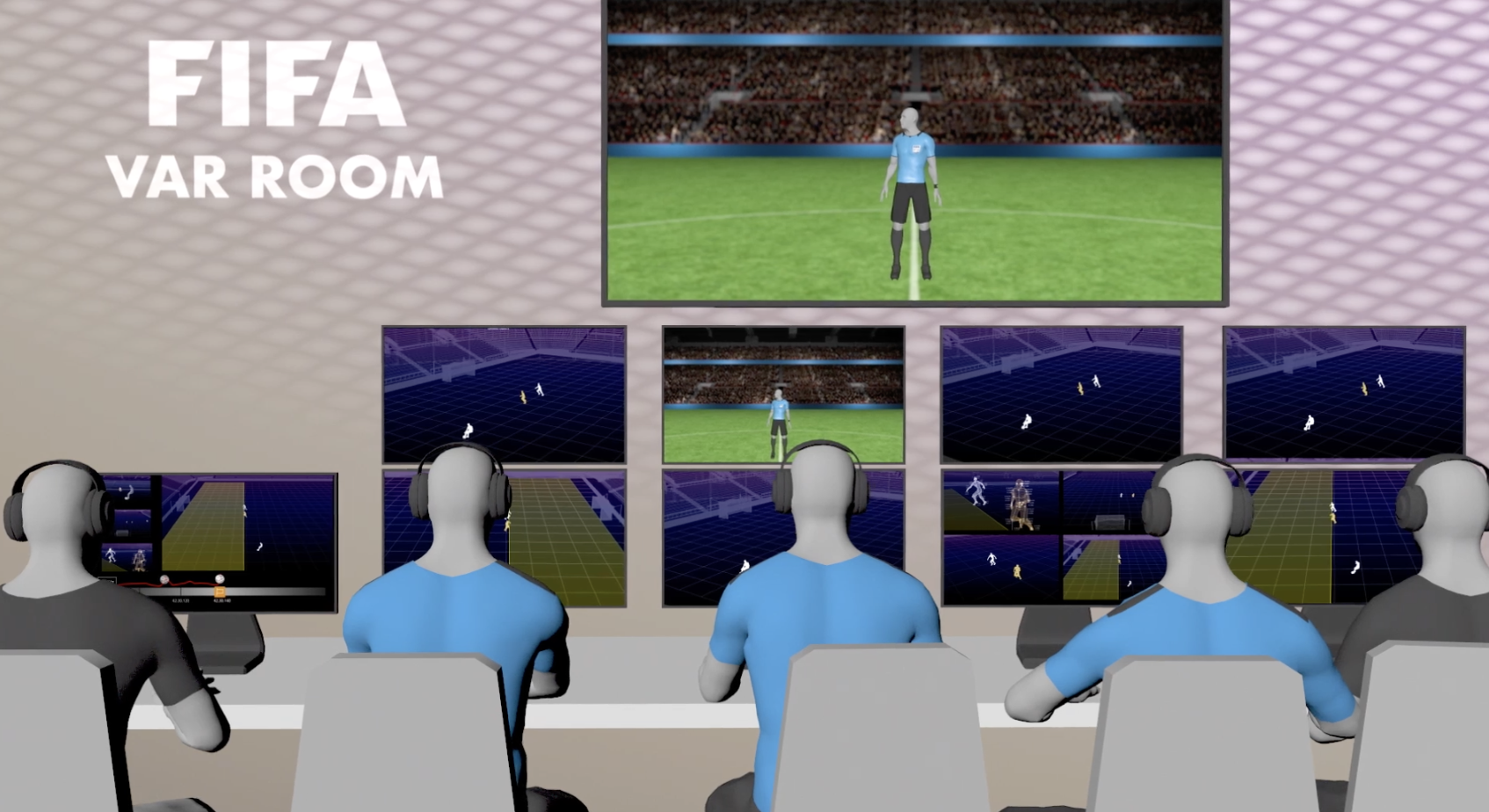
Traditional VAR systems work well, but they have certain limitations. For example, the accuracy of these systems is not great, and they also disrupt the game with lengthy reviews. Integrating computer vision into these systems is a great way to mitigate these concerns. The core technology driving this advanced VAR system would be video and image recognition.
By treating each video as a sequence of images, computer vision systems can extract crucial data to make accurate decisions for every situation. Maybe one day, instead of being an assistive technology, vision-aided VAR can be fully automated to make precise decisions in mere seconds.
Performance Analytics
Computer vision can analyze high-resolution video footage to track an athlete playing in a game, their overall performance, and the performance of a team as a whole. This data-driven approach can be used to assess game strategies, devise new training methods for players based on their performance, and ultimately elevate the performance of the entire team.
Coaches and trainers can use this technology to make customized training routines based on areas that need improvement. As the technology continues to advance, it will reshape the sports industry, setting new standards for training, competition, and fan engagement.
Enhancing Fan Experience through Computer Vision
Another important use case of computer vision in sports is elevating the fans' experience. Let’s take a closer look at how it’s done.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) provide an immersive and interactive fan experience. VR transports fans to the heart of the action, allowing fans to watch the games from unique perspectives. VR technology with real time computer vision capabilities can be used by fans to participate in virtual events and interact with players and other fans.
AR, on the other hand, complements VR by enhancing the real-world experience with digital features overlaid over it. AR can provide fans with additional information like game statistics, and interactive elements, such as games, quizzes, and filters. For example, the Apple Vision Pro AR glasses can be used to watch your favorite sport while having different statistics analysis data displayed next to the sport.
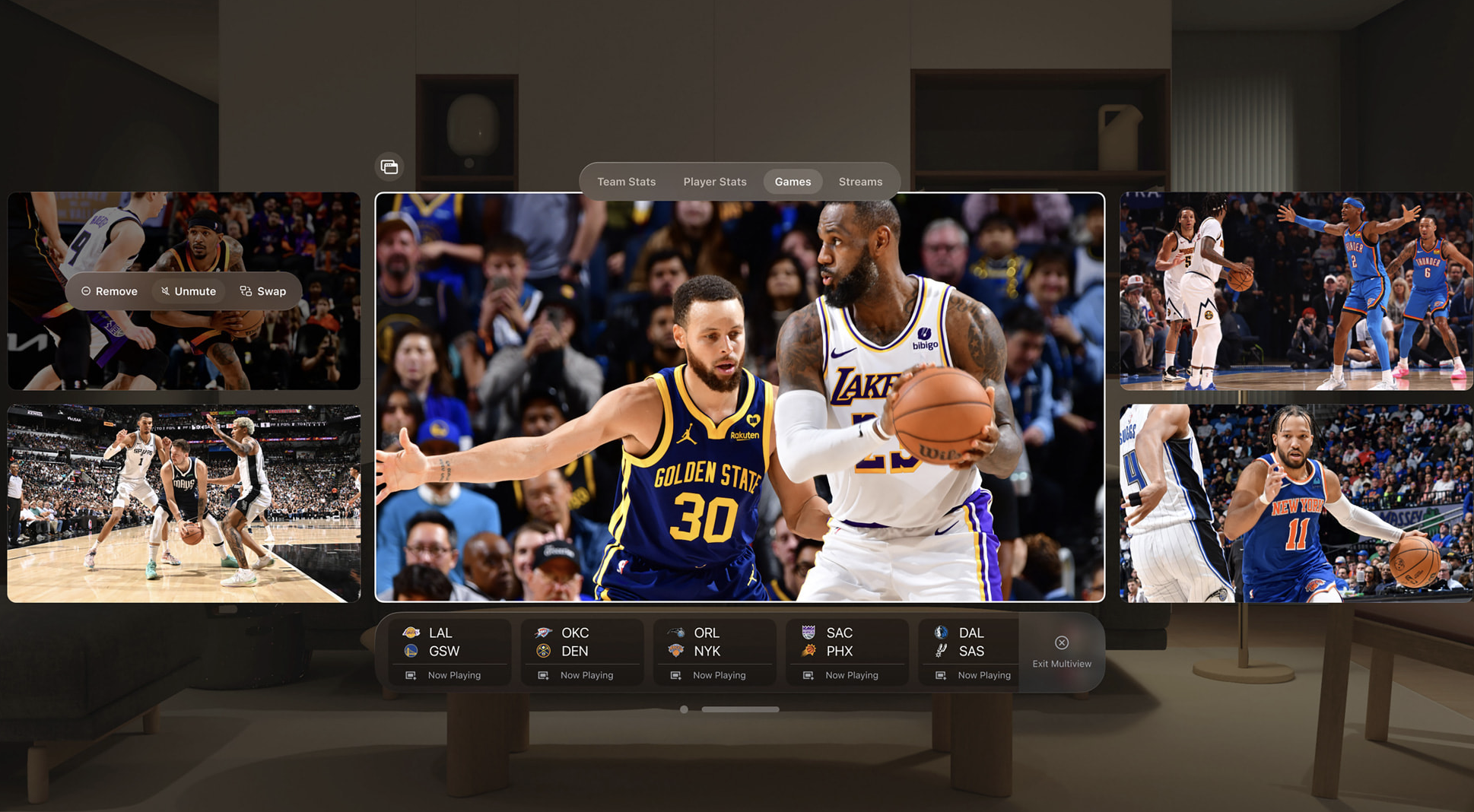
Computer vision is also transforming the field of sports broadcasting, as well as elevating stadium experience. By analyzing live footage, real time insights like game statistics, player information, and key moments of the game can provided to the broadcasting officials for live broadcast. These data can also be displayed on screens within the stadiums to enhance the viewing experience of live audiences. Beyond entertainment, computer vision systems can act as an extra set of eyes in stadiums to monitor the behavior of the fans, detect suspicious incidents, etc.
Technologies Powering Computer Vision in Sports
Now that we’ve covered some of the applications of computer vision in sports, let’s explore the technologies that make it all possible.
The foundation of computer vision systems in sports lies in capturing high quality visual data. A variety of high-resolution camera systems, including 2D and 3D cameras, are used to capture the data. 2D cameras provide a basic understanding of the scene in two dimensions, while 3D cameras capture the depth as well, which is used for accurate measurement of distance.
Cameras with a higher frame rate are also used for capturing more detail during fast paced action like dribbling or goal scoring. Sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes are also used to get additional data on player movement.
After capturing the visual data, machine learning, and deep learning algorithms are used to process and interpret the data. These algorithms are the core technology behind computer vision. They are trained on vast datasets of labeled images to learn patterns and to make predictions based on them.
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) are deep learning architectures that are used for tasks like object detection, image recognition, and classification. For example, deep learning models like YOLO are used for real time object detection tasks, such as player and ball detection.
Processing large amounts of visual data is a very challenging process, especially when it comes to latency. Sports broadcasting and analytics require real time data processing, so using cloud computing may not be an option due to delays.
Edge computing can be adopted to ensure low latency and real-time analysis during live games. It involves processing data closer to the source, such as at the stadium or arena. This reduces the need to transmit large amounts of data to a centralized cloud for processing, resulting in faster insights and decision-making.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Let’s explore how computer vision technology is used in some of the world's most popular sports events.
The 2024 Paris Olympics
The 2024 Paris Olympics showcased not only some of the best athletic talents from around the world but some of the latest technological innovations as well. One such technology was computer vision, which was used to accurately track athletes and to record various performance metrics.
This made way for an in-depth analysis of each event, helping broadcasters tell a detailed story of how an athlete won or lost an event. All of the visual data was captured using high-definition cameras installed around the field of play, and the data was fed to AI models that were specifically trained for each sport, including:
- Volleyball: Computer vision was used to calculate the distances covered by each player, the speed of the players and the ball, the unique player techniques, including jump heights, and the type of shots, from smashes to blocks and spikes.
- Aquatic Events: Divers were tracked using computer vision from the moment they began their dive to their entry into the water. The collected data is used to create 3D graphics of the dive with metrics like airtime and speed.
- Gymnastics: The height and airtime of the skills performed were measured using computer vision. Human pose estimation or skeleton tracking techniques were also used to track the movements of the athlete; even the angles of the athlete’s feet were detected using these systems.
Offside Detection in Football
Delivering accurate offside decisions in football has always been challenging and, at times, controversial. To avoid such issues, a new computer vision-based system, known as semi-automatic offside technology (SAOT), was introduced. After its successful debut at the 2022 FIFA World Cup, the technology is currently being used for the 2024-2025 English Premier League.
In football, a player is considered offside if they are in front of the last defender (not including the goalkeeper) when the ball is passed to them. SAOT uses a suite of cameras installed around the stadiums with computer vision technology to track player movements and the ball’s position. This system can determine offside calls by drawing virtual lines to show the precise position of the attacking player relative to the last defender.

Identify Track Violations in Formula One
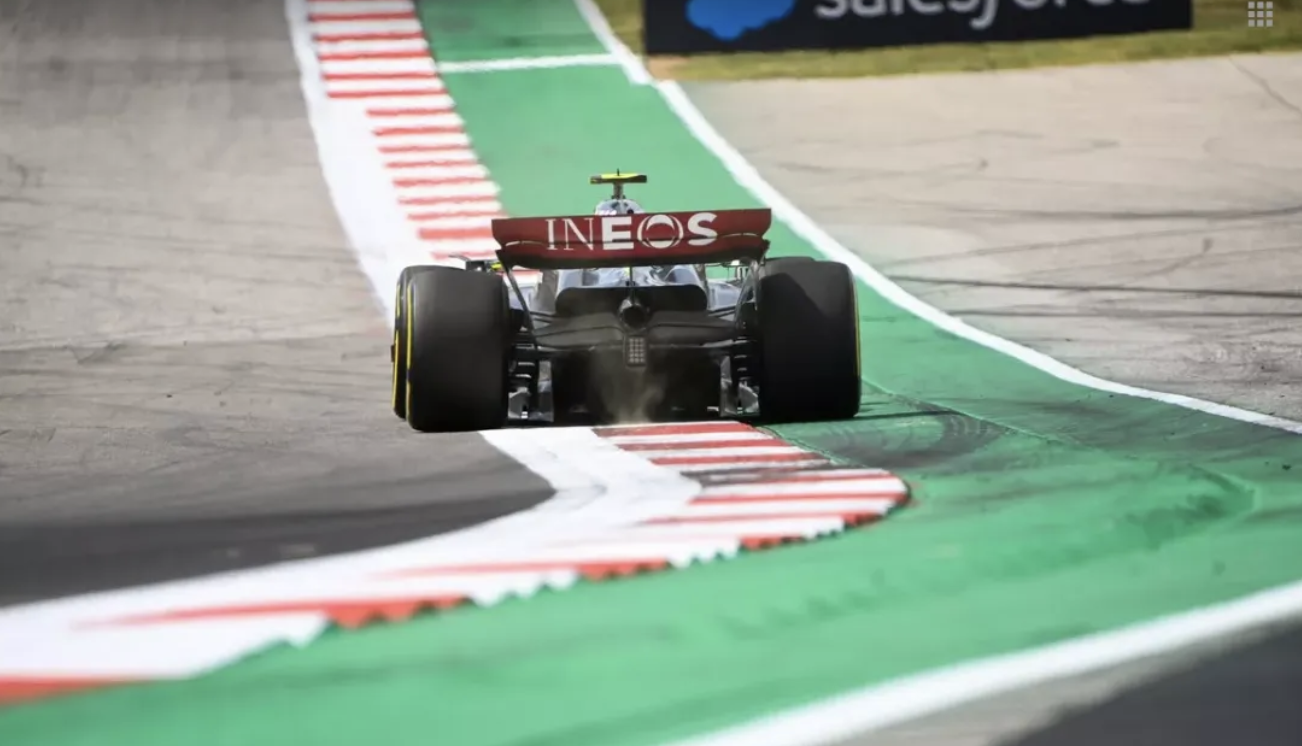
Similar to offside decisions in football, decisions on track violations in Formula One racing are also a subject of controversy. A track violation is given to drivers who cross the track limits, which are boundaries of the circuit that the drivers must respect and not exceed (they are marked by white lines).
To solve the issues related to deciding track violations, the governing body for world motorsport, Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA), has decided to use a computer vision system. The system will allow the FIA to automatically detect when a car’s wheels have completely crossed the boundaries.
The system works by analyzing video footage taken by high-resolution cameras placed at strategic locations around the track (especially in corners). The collected video footage is then fed to the computer vision models for frame-by-frame analysis. Techniques like edge detection, contour detection, and pixel counting are used to detect the boundaries and cars within the footage. If a violation has been detected, the FIA will get alerts.

Conclusion
Computer vision is transforming the sports industry in a lot of innovative ways. It helps boost the performance of players, improves decision-making during games, and enhances fan engagement. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises more personalized training, real-time insights, and much more immersive experiences using technologies like AR. Its impact is clear; providing fresh perspectives, raising competition standards, and paving the way for a future where technology and sports go hand in hand.
Keep Reading
Check out these resources to keep expanding your horizon on computer vision in sports:
- Blog post on the top 7 sports datasets for computer vision projects.
- Roboflow’s GitHub repository on sports.
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Contributing Writer. (Nov 5, 2024). Computer Vision Use Cases in Sports. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/computer-vision-use-cases-in-sports/
