
In this tutorial, we walkthrough how to train YOLO26 for object detection on a custom dataset.
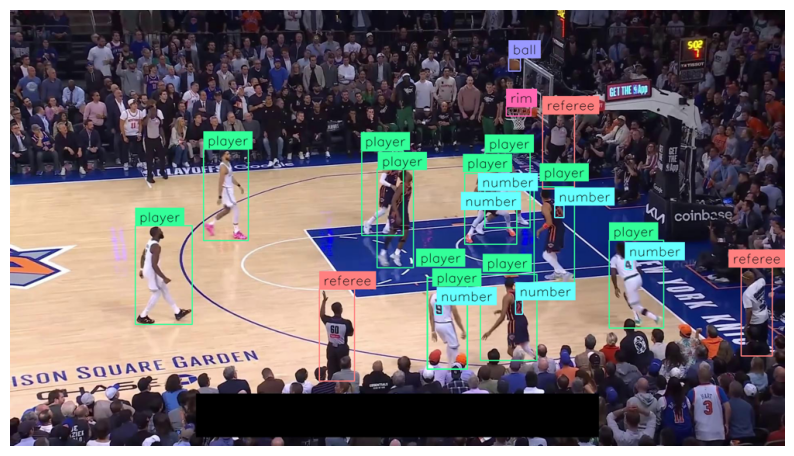
We recommend working through this blog post side-by-side with the YOLO26 Object Detection Colab notebook. You'll learn how to train a custom model to detect NBA players, referees, and basketballs.
Set up the Colab Notebook
Before we start training the model, we'll need to set hardware accelerator to GPU. We can do that inside the Colab Notebook by going to Edit -> Notebook settings -> Hardware accelerator and select the GPU option
Installing required packages
Now let's install the required packages - specifically ultralytics, supervision, and roboflow.
pip install "ultralytics>=8.4.0" supervision roboflowYOLO26 custom dataset
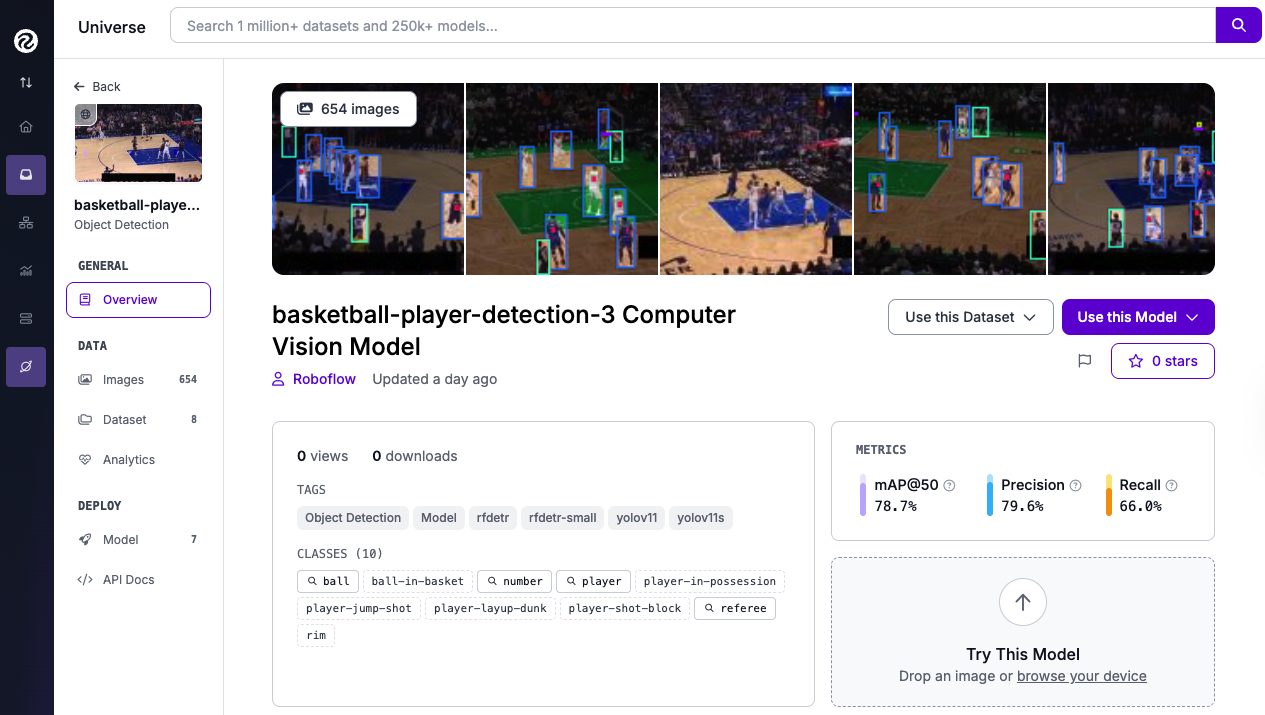
We'll be custom-training the YOLO26 object detection model on the Basketball-Player-Detection dataset, found on Roboflow Universe. It contains 654 annotated high-resolution images, and can be downloaded with the roboflow library.
To download the dataset, we'll need to copy the Roboflow API key into the Colab 🔑 Secrets store, under the name ROBOFLOW_API_KEY.
Train YOLO26 on a custom dataset
Now we're ready to download the dataset and train the YOLO26 model. After installing the required libraries, we can skip the Inference with model pre-trained on COCO dataset and go straight to Fine-tune YOLO26 on custom dataset.
from google.colab import userdata
from roboflow import Roboflow
ROBOFLOW_API_KEY = userdata.get('ROBOFLOW_API_KEY')
rf = Roboflow(api_key=ROBOFLOW_API_KEY)
workspace = rf.workspace("roboflow-jvuqo")
project = workspace.project("basketball-player-detection-3-ycjdo")
version = project.version(10)
dataset = version.download("yolov11")The script above will download the basketball dataset (with YOLOv11 annotation format) from the Roboflow Universe. And after downloading is complete, we can go ahead and start fine-tuning the YOLO26 for 20 epochs, which will take a few minutes:
yolo task=detect mode=train model=yolo26m.pt data={dataset.location}/data.yaml epochs=20 imgsz=640 plots=TrueInference with a custom YOLO26 model
After the model finishes training, you'll have training results and fine-tuned model weights. We can see how the mean average precision (mAP) was steadily rising throughout the 20 epochs.
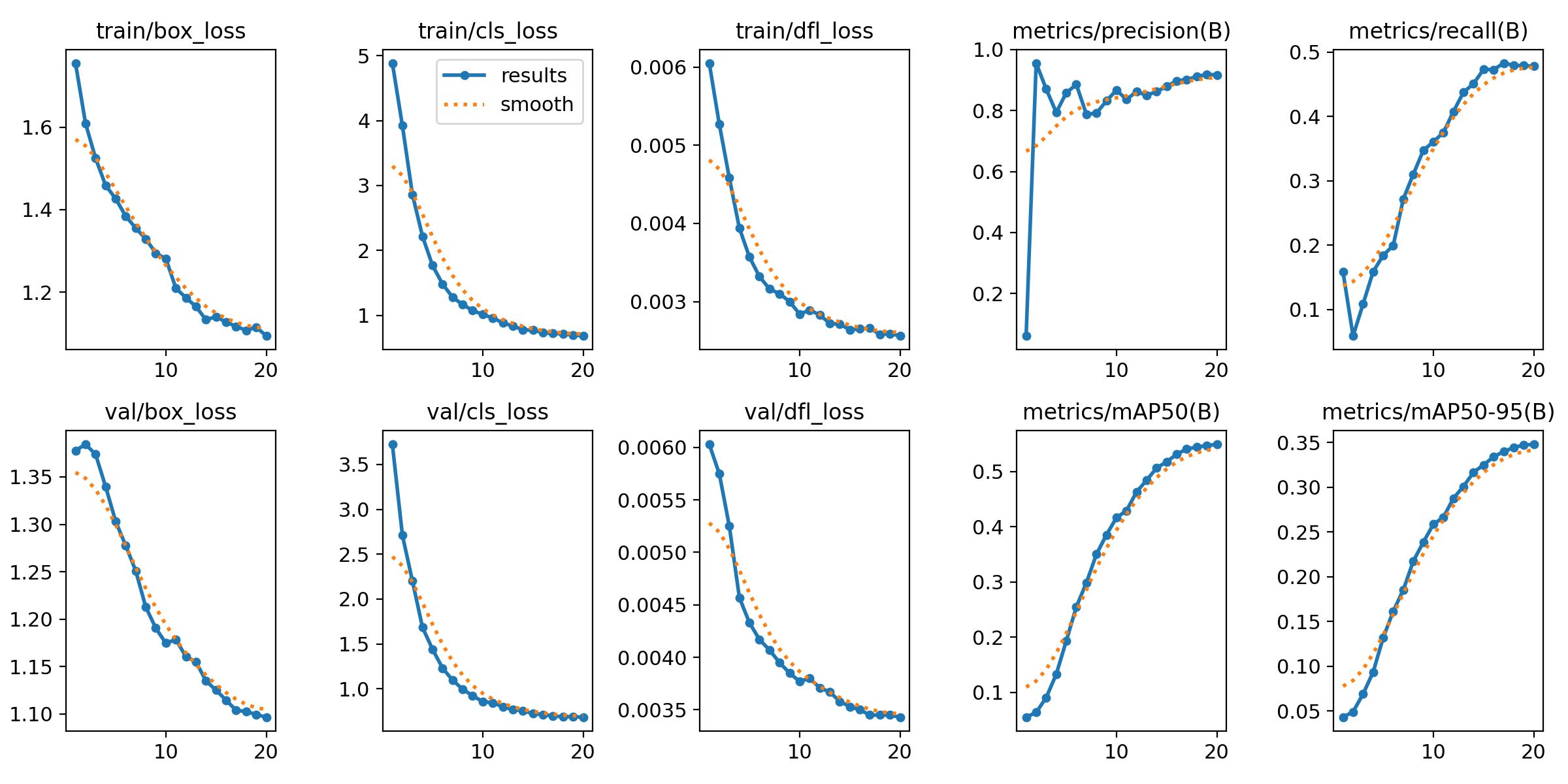
20 epochs completed in 0.147 hours.
Optimizer stripped from /content/runs/detect/train/weights/last.pt, 44.0MB
Optimizer stripped from /content/runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt, 44.0MBIn the training logs, you can see where the fine-tuned model weights (best.pt) are located, which we can use for local inference on the Colab notebook.
Inference with a custom model
We can load the best.pt weights into the YOLO() and run model.predict() to run object detection model inference on our image from the Basketball dataset. We'll use supervision for visualization of the object detection model results using bounding boxes and their class id.
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ultralytics import YOLO
from PIL import Image
model = YOLO(f'{HOME}/runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt')
# Randomly select one image from the dataset
idx = random.randint(0, len(ds_test) - 1)
path, _, annotations = ds_test[idx]
# Load and run inference
image = Image.open(path)
result = model.predict(image, verbose=False)[0]
detections = sv.Detections.from_ultralytics(result)
# Annotate (visualize bounding boxes) the image
annotated_image = annotate(image, detections)
# Display the annotated image
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(annotated_image)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()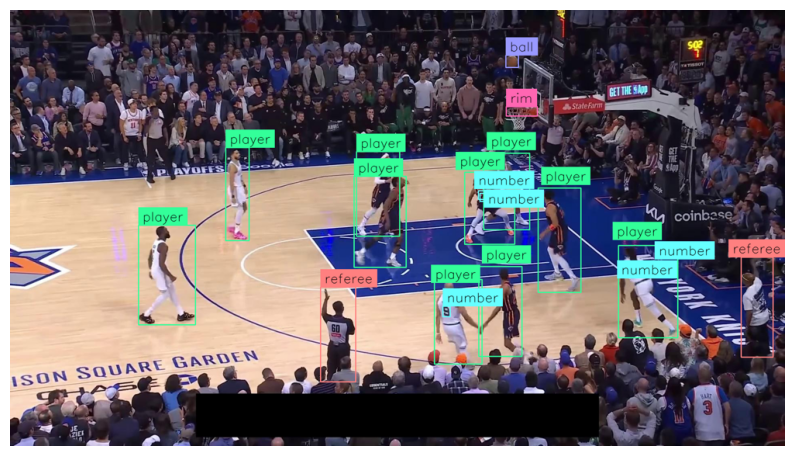
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully fine-tuned the YOLO26 architecture to detect specific objects within a custom dataset. This workflow provides a scalable foundation that you can easily adapt to solve unique computer vision problems across industries.
Now that you know how to train the latest YOLO model, explore new datasets on Roboflow Universe and build your next vision AI application.
Try YOLO26 on Images
See how YOLO26 performs on images for common objects included in the COCO dataset. Test out how the model handles your data below.
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Erik Kokalj. (Jan 14, 2026). How to Train a YOLO26 Object Detection Model with Custom Data. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/how-to-train-yolo26-custom-data/
