
Computer vision applications are reshaping industries worldwide, improving efficiency, safety, and quality in ways that were previously unimaginable. By enabling machines to interpret and understand visual data, computer vision is facilitating innovations that are streamlining processes, improving decision making, and transforming how businesses operate.
Computer vision can detect chemical corrosion on manufactured parts, keep baby piglets safe from a sleeping mother sow, ensure a pickleball isn't out of bounds, and even alert you when there's a new package at your door.
Let's explore some popular computer vision applications in construction, robotics, manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and beyond.
Popular Computer Vision Applications
Computer vision is being used in industries from construction to agriculture and even sports. Here we'll take a look at ten popular applications.
1. Construction computer vision applications
In the construction industry, computer vision has many applications, ensuring projects stay on schedule and meet quality standards. Vision AI is transforming how projects are managed, monitored, and maintained. Construction companies can now automate tasks such as monitoring construction progress, inspecting equipment, and ensuring site safety. Here are a few common construction uses:

- Floor plan analysis: Floor plans are crucial for creating understanding spaces in interior design, architecture, and construction projects. Traditionally, analyzing floor plans required painstaking manual effort from a select few experts, draining time and resources. With computer vision, you can automate and scale floor plan analysis.
- Equipment and structural inspection: Detect wear and tear, cracks, and structural weaknesses in machinery, roads, bridges, and buildings using machine vision, reducing maintenance costs and preventing failures. For example, here's a study benchmarking YOLOv8 for optimal crack detection in civil infrastructure.
- Site safety monitoring: According to the Center for Construction Research and Training, struck-by accidents are a leading cause of death on construction sites. Computer vision can be used to identify safety hazards such as workers without PPE, unsafe scaffolding, equipment malfunctions, and potential collision risks to prevent accidents and improve compliance.
2. Aerospace computer vision applications
Computer vision is playing a pivotal role in the aerospace industry, revolutionizing operations from assembly lines to predictive maintenance. Computer vision applications in aerospace help businesses meet quality control standards, operationalize plane assembly, and manage defect detection and part identification on assembly lines. A couple popular aerospace applications include:
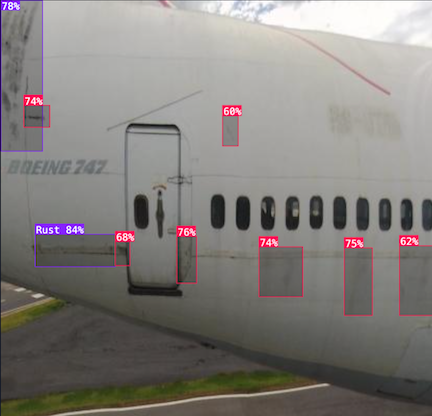
- Defect detection: Computer vision enables the identification of defects in critical aircraft components, which is crucial to maintaining the safety and longevity of the aircraft. For instance, cracks in turbine blades, corrosion in fuselage panels, or misalignments in structural components can be automatically detected through high-resolution imaging and AI-powered analysis.
- Autonomous navigation: Computer vision is advancing autonomous navigation in aerospace, especially in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and drones. By training AI models to interpret satellite imagery, perform real-time obstacle detection, and enable autonomous flight navigation, computer vision aids in improving safety and efficiency during flights. These systems can autonomously detect and avoid obstacles, enhancing the capabilities of UAVs used in surveillance, cargo delivery, and environmental monitoring. Learn more about how to train computer vision models on aerial imagery.
- Predictive maintenance: Computer vision is also integral to predictive maintenance in the aerospace industry. By categorizing and analyzing wear patterns in aircraft engines, landing gear, and other critical systems, AI models can identify potential issues before they lead to major failures. For instance, GE Aerospace uses AI for predictive maintenance “...we are able to detect through analytics and through AI models an anomaly on an oil filter sensor [if] the signal that we are getting back is not in the normal parameters."
3. Transportation computer vision applications
In the transportation and automotive industries, computer vision is driving innovation, changing how vehicles navigate and interact with their surroundings. From autonomous vehicles to smart parking solutions, computer vision is playing an essential role in improving the efficiency and safety of transportation systems.
There are applications within vehicles as well: Amazon is expected to deploy 1,000 electric delivery vans with vision-assisted package retrieval by early 2025. Here are some use cases:

- Autonomous vehicles: With Waymo cars already on the road, the future of self-driving cars is no longer a distant dream but a rapidly approaching reality. In the 1980s, the pace of innovation in the field quickened with the DARPA-funded Autonomous Land Vehicle project, which marked the first successful attempt at autonomous navigation using computer vision and sensors. Using computer vision today, cars can now spot road signs, other vehicles, and pedestrians. Advanced algorithms analyze road markings to keep the vehicle within its lane and manage lane changes. And by analyzing visual data, computer vision systems estimate the distance to objects, aiding in functions like adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance.
- Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS): Tesla's Autopilot is an example of an advanced drive assistance system. ADAS uses computer vision to enhance vehicle safety and automate driving tasks. Features like lane departure warning, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control rely on cameras and AI to detect vehicles, pedestrians, and road signs.
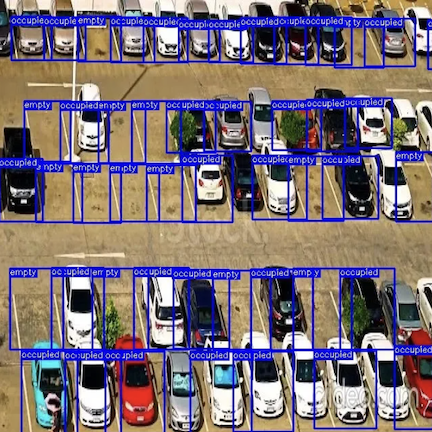
- Parking lot management: Computer vision can lead to smart parking lot management. Cameras and computer vision algorithms can work together in parking lots to know if a vehicle has occupied a parking space or not. Vision AI can even help read license plates, track vehicles, and send alerts.
4. Manufacturing computer vision applications
By integrating vision AI, manufacturers can enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and maintain consistent product quality. With an AI-powered visual inspection system manufacturers can examine product specifications such as dimensions, color accuracy, and more. Some common manufacturing use cases include:
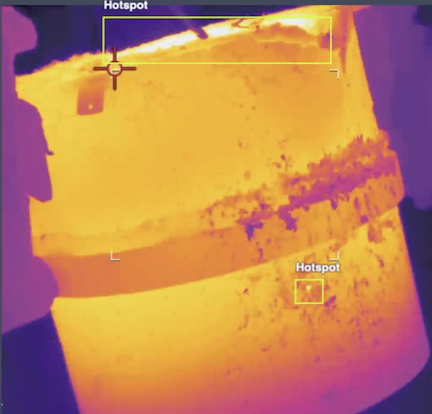
- Automated quality inspection: Edge AI can rapidly detect defects, missing components, or counterfeit parts in products. For example, an x-ray-based system can identify missing screws or counterfeit batteries in electronic devices with high precision, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Workplace safety monitoring: The most recent data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reveals a staggering 2.6 million nonfatal injuries and illnesses recorded annually. On top of that, 82% of companies have faced at least one unplanned downtime incident over the past three years, leading to significant productivity losses. Vision AI can monitor manufacturing floors in real time to ensure workers are following safety protocols, such as wearing protective gear and maintaining safe distances from hazardous machinery. Computer vision can also help monitor the flow of employees and machinery to prevent collisions. This can reduce workplace accidents and ensures compliance with regulations.
- Inventory and supply chain tracking: Whether you’re a factory manager looking to improve inventory management or a store owner striving to prevent stock outs, real-time data can be a game-changer. AI-powered vision systems can automatically count parts, track items on conveyor belts, and verify shipments. By using cameras and AI to monitor stock levels and logistics, manufacturers can reduce errors and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance: The hourly cost to a business of equipment going down and work stopping ranges from $36,000 in fast-moving consumer goods to $2.3 million in the automotive sector, according to a 2024 Siemens report. By analyzing equipment wear and tear through visual inspection, computer vision can detect early signs of mechanical failure. This enables manufacturers to perform maintenance before a breakdown occurs, minimizing downtime and costly repairs. For example predictive maintenance AI at at BMW Group Plant Regensburg avoids an average of around 500 minutes of disruption per year in vehicle assembly at the Regensburg plant alone.
5. Agriculture computer vision applications
Pests destroy about 40% of global agricultural productivity, costing the agriculture industry over $70 billion every year. But thanks to advancements in computer vision, farmers can now identify and eliminate these destructive pests with precision.
With computer vision, farmers can improve efficiency, reduce waste, and safeguard their harvests. Here are a few ways the agriculture industry is harnessing computer vision:
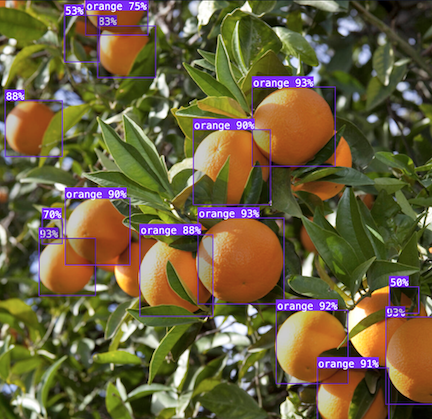

- Precision planting and row monitoring: By analyzing drone or satellite images, computer vision can help ensure crops are planted with optimal spacing to maximize yield. AI models can also assist disease detection - monitoring plant to identify subtle disease symptoms such as leaf discoloration, spots, lesions, and wilting with precision. Vision AI is used in predicting overall crop yields too, by analyzing the number of mature fruits or vegetables present in a field, giving farmers a more accurate forecast of their harvest.
- Automated weed detection and targeted spraying: Weed species reduce plant production by about 31.5% each year, leading to economic losses of about $32 billion annually. Traditional weed control methods rely heavily on manual labor or indiscriminate herbicide spraying. Now AI-powered vision system can accurately distinguishing between crops and weeds at scale. AI-powered cameras on drones or tractors can identify weeds in fields and direct herbicides only where needed. This reduces chemical use, saves costs, and improves sustainability.
- Livestock management: Computer vision can monitor the health and well being of animals. For example, around 50% of the postnatal death in piglets is caused by crushing or overlying by the domestic sow. With computer vision, alerts can be sent when there's a piglet at risk.
6. Medical computer vision applications
Healthcare and medicine applications of computer vision are vast. Medical imaging is becoming more precise, diagnostic processes are more efficient, and treatments are better targeted. Discover some of the ways medical care is being impacted by computer vision:
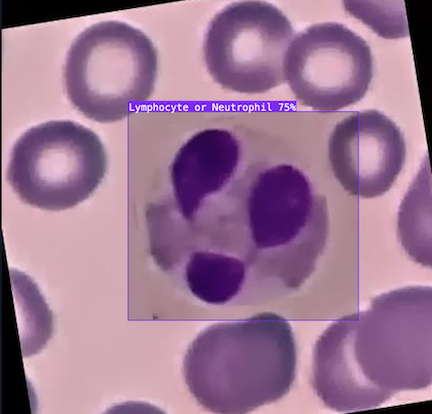
- Automated cell counting to accelerate cancer research: At a Danish university, researchers studying cancer needed to identify when neutrophils - specific white blood cells - became activated. Manually counting hundreds of these cells was an incredibly slow and tedious process, often taking 40 to 60 hours between trial runs. By developing a computer vision model to automatically detect and count neutrophils, this process was reduced to under 30 seconds. Now researchers can instantly visualize neutrophil activation, allowing them to analyze cellular responses to different drugs or compounds more efficiently.
- Enhancing radiology: Computer vision is increasingly being used to support radiologists and improve diagnostic accuracy. As just one example, in the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic when testing infrastructure was severely limited, an open dataset available on Roboflow enabled users to build models that could distinguish between COVID-19, pneumonia, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and healthy chest scans.
- Medical diagnosis: Beyond that, a groundbreaking study demonstrated that an AI model could diagnose skin cancer from images more accurately than top dermatologists. By integrating this capability into a mobile app, AI-driven diagnosis became more accessible, empowering both healthcare professionals and patients to detect potential skin conditions early.
- Improving quality assurance in drug production: Beyond research and diagnostics, computer vision plays a crucial role in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Vision AI is being used for quality assurance in vaccine production—ensuring that syringes contain the correct liquid volume, that stoppers are properly sealed, and that doses meet regulatory standards. These applications help streamline production, reduce human error, and improve overall healthcare outcomes.
7. Retail computer vision applications
Computer vision applications are transforming the retail landscape, helping businesses enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and improve efficiency.
Computer vision is helping to reduce theft, ease the checkout experience and help customers in-store. Toshiba's Modular eXpansion Platform harnesses computer vision to allow business owners to tailor a self-checkout solution that’s unique to their specific retail environment, and features built-in fraud detection to catch incorrect scans or product misplacements. Here are some additional applications for computer vision in retail:

- Streamline with smart checkout: Computer vision software can automatically recognize products being purchased. Here’s an example of a self-checkout system built in just 10 minutes with Roboflow. Sam’s Club introduced AI-powered exit technology using computer vision to seamlessly confirm members have paid for all items in their shopping carts – without requiring an associate to check members’ purchases before leaving the club. This translates to all members leaving the club 23% faster.
- Real-time store traffic and foot path analysis: By recognizing footpaths, a computer vision model can help you gain insights into high-traffic areas, peak shopping hours, and customer behavior to better inform your product placement and staffing decisions. By putting high-margin or promotional items in high-traffic areas, retailers can increase sales and improve customer experience.
- Barcode scanning and defect detection: For retailers that receive goods from third parties, computer vision software can easily read part and SKU number as incoming deliveries arrive with OCR, checking for discrepancies between orders and shipments. It can also inspect packages for signs of damage or mislabeling.
8. Robotics applications across industries
Robots can identify and interact with objects in their environment with the help of computer vision. For example, researchers have developed a deep learning model that enables robots to skillfully grasp objects in cluttered environments by predicting the optimal grasp points using visual data, which could be useful in industrial automation. Multi-stage long-horizon robotic manipulation models are helping robots build and use motor skills.

Medical robotics are being studied in order to enhance a surgeon's ability to maneuver instruments within the human body with greater precision. And in agriculture, advanced computer vision algorithms are leveraged to autonomously identify and harvest fruits.
Using a combination of robotics and wheeled locomotion technology, Hyundai New Horizons Studio's vehicles are expected to redefine vehicular mobility - for example, a car with robotic legs could save lives as the first responder in natural disasters; or, people who do not have access to an ADA ramp could hail a car to walk up to their front door, level itself, and allow wheelchairs to roll right in.
9. Animal monitoring with computer vision
Computer vision applications are making significant strides in animal monitoring, revolutionizing wildlife conservation efforts and enhancing our understanding of animal behaviors across both land and sea. Here are some animal-centric computer vision applications:

- Wildlife conservation: In wildlife ecology, computer vision aids in classifying species from images, providing consistent and efficient data collection methods for research. And automated analysis of trail-camera images enables researchers to monitor animal populations, track movements, and study behavioral patterns without extensive manual effort.
- Marine animal monitoring: Computer vision is used to track marine animals like fish, whales, and sea turtles in their natural environments. Through underwater cameras and visual recognition algorithms, researchers can go where they physically can't - monitoring species movements, feeding behaviors, and interactions with their ecosystem. This helps scientists better understand migration patterns, breeding habits, and how marine animals respond to environmental changes such as climate change or human activity.
10. Augmented reality (AR) applications
The global augmented reality market is expected to grow from $62.75 billion in 2023 to 1,869.40 billion by 2032. Computer vision is a key part of AR's ability to integrate digital content into real-world environments.
For example, the National Gallery in London used augmented reality to take its collections beyond its walls which users viewed by pointing their devices at specific areas, which computer vision identified and detected. Classic paintings and modern works from artists including Titian, Vincent Van Gogh, and Georges Pierre Seurat appeared on London’s busy streets with their augmented reality app.

Vision AI also assists with depth estimation and gesture recognition necessary for AR. In AR gaming, such as Pokémon Go, virtual creatures are placed in the real world, and computer vision ensures they appear realistically on the ground or interact with real-world obstacles. Another example is furniture company CB2, which has an app that allows potential buyers to visualize how furniture will look in their space.
Create Computer Vision Apps
Computer vision applications are changing the ways we work. Ready to learn more about how AI could impact your industry? Roboflow is free to get started and easy to scale up. We’re SOC 2 Type II compliant, support custom security rules, and power customers operating at global scale with terabytes of data today. Learn more about how Roboflow Enterprise can bring computer vision solutions to your business. Talk to an AI expert to discuss your unique use cases.
Keep reading: Explore computer vision examples.
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Trevor Lynn. (Mar 11, 2025). Computer Vision Applications. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/computer-vision-applications/
