
YOLO26 was released on January 14th, 2026, and we are excited to announce that the latest YOLO model is fully supported on the Roboflow platform for labeling, training, and deployment.
YOLO26 is the latest evolution of real-time computer vision models. Optimized specifically for edge deployment and CPU performance, YOLO26 introduces significant architectural changes, including the removal of Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) for end-to-end predictions and the new MuSGD optimizer, making it one of the fastest and most efficient YOLO models available today.
Deploy YOLO26 Models with Roboflow
YOLO26 models are available for deployment in the cloud or on your own hardware using Roboflow Inference. Because YOLO26 is optimized for edge devices, we highly recommend deploying it on-device for the lowest latency. Roboflow Inference supports YOLO26 out of the box.
To deploy a YOLO26 model on your own hardware (CPU or GPU), first install the Inference and Supervision:
pip install --upgrade inference supervisionYou can run Inference in two ways:
- In a Docker container, or;
- Using our Python SDK.
For this example, we are going to deploy with the Python SDK.
Create a new Python file and add the following code:
from inference import get_model
from inference.core.utils.image_utils import load_image_bgr
import supervision as sv
# Download the image for inferencing
image = load_image_bgr("https://media.roboflow.com/notebooks/examples/dog.jpeg")
# load a pre-trained yolo26 large model
model = get_model(model_id="yolo26l-640")
# run inference on our chosen image, image can be a url, a numpy array, a PIL image, etc.
results = model.infer(image)[0]
# load the results into the supervision Detections api
detections = sv.Detections.from_inference(results)
# create supervision annotators
bounding_box_annotator = sv.BoxAnnotator()
label_annotator = sv.LabelAnnotator()
# annotate the image with our inference results
annotated_image = bounding_box_annotator.annotate(
scene=image, detections=detections)
annotated_image = label_annotator.annotate(
scene=annotated_image, detections=detections)
# display the image
sv.plot_image(annotated_image)If you want to use a custom model (that you trained on a dataset), replace the model_id with your own model ID and add the API key.
Use YOLO26 in Roboflow Workflows
YOLO26 is also fully integrated into Roboflow Workflows, our web-based application builder. You can use YOLO26 as the detection step in complex, multi-stage computer vision pipelines and combine the model with logic, other models (like CLIP or SAM), and third-party integrations.
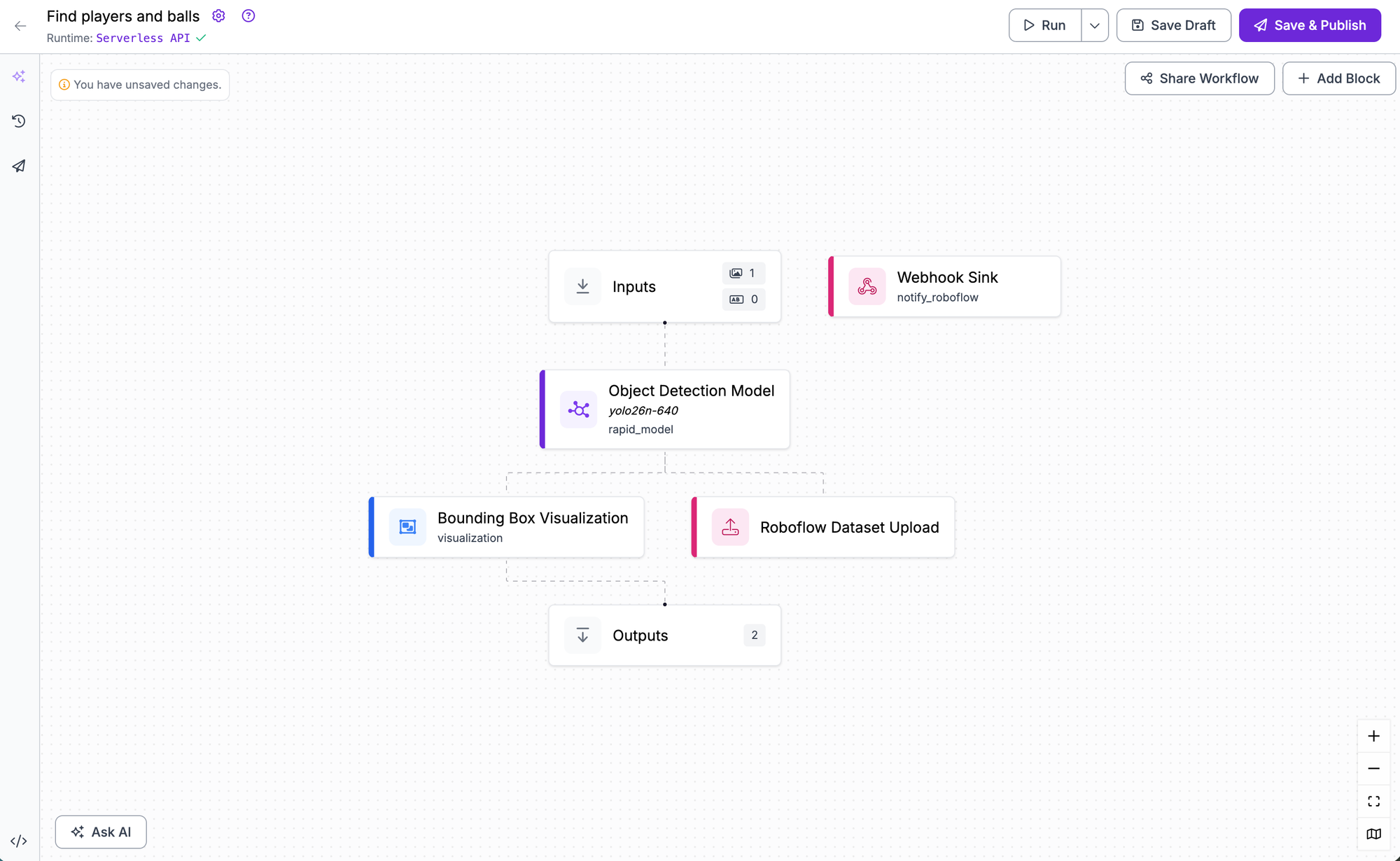
To use YOLO26 in a Workflow, navigate to the Workflows tab in your dashboard and create a new Workflow. Add a model block and select your trained YOLO26 model.
Train YOLO26 Models with Roboflow
You can train YOLO26 object detection, instance segmentation, and keypoint detection models directly on the Roboflow-hosted platform using Roboflow Train. This allows you to fine-tune the model on your custom dataset with just a few clicks, no hardware setup required.
Once you have a labeled dataset (either from your own data or from Roboflow Universe), generate a version of your dataset to apply pre-processing and augmentations if needed. Then, click Train with Roboflow in the model selection window and choose YOLO26.
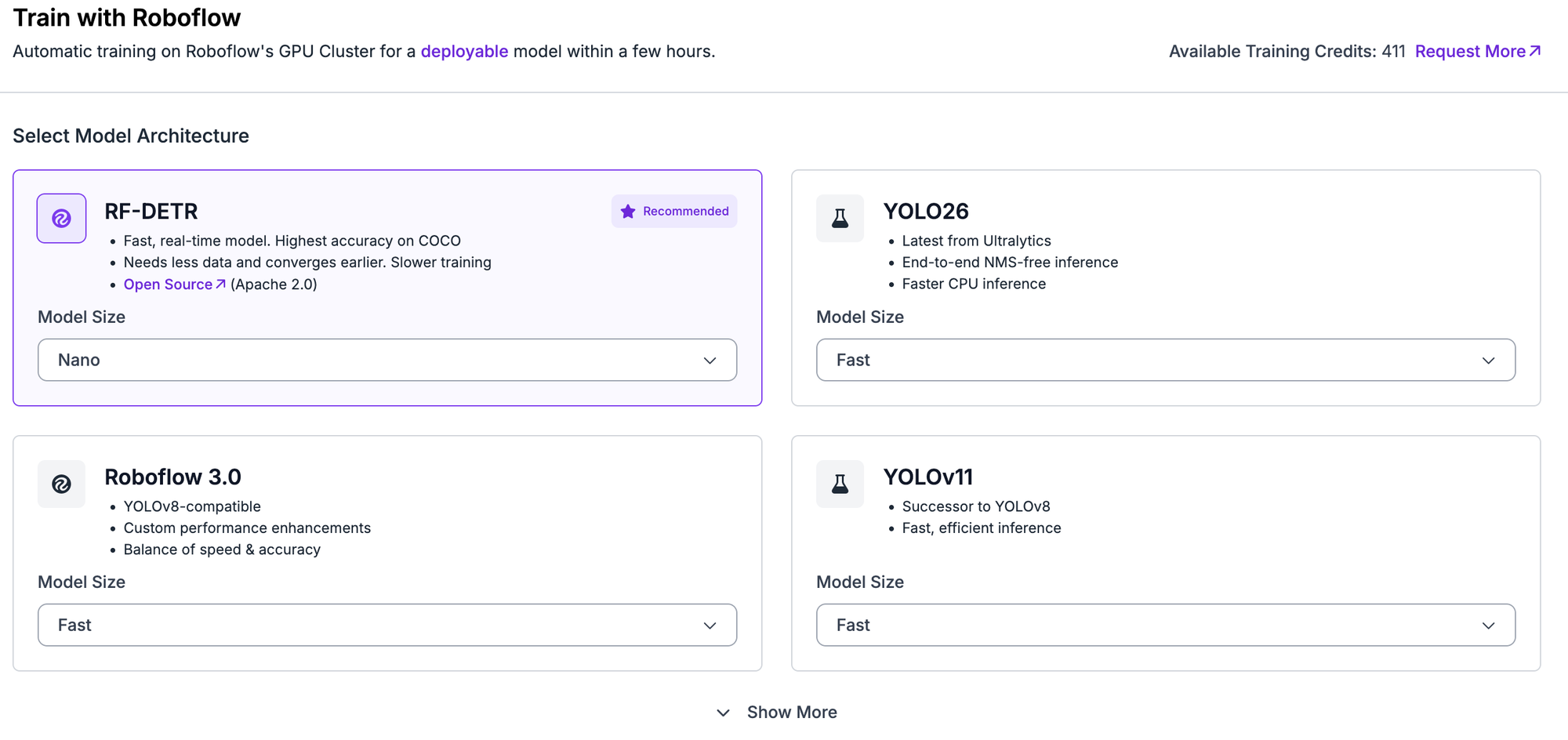
You can choose between different model sizes, including Nano (N), Small (S), Medium (M), Large (L), and Extra Large (X). Refer to the YOLO26 performance table in the post to understand the various sizes and speeds so you can choose the best model for your use case.
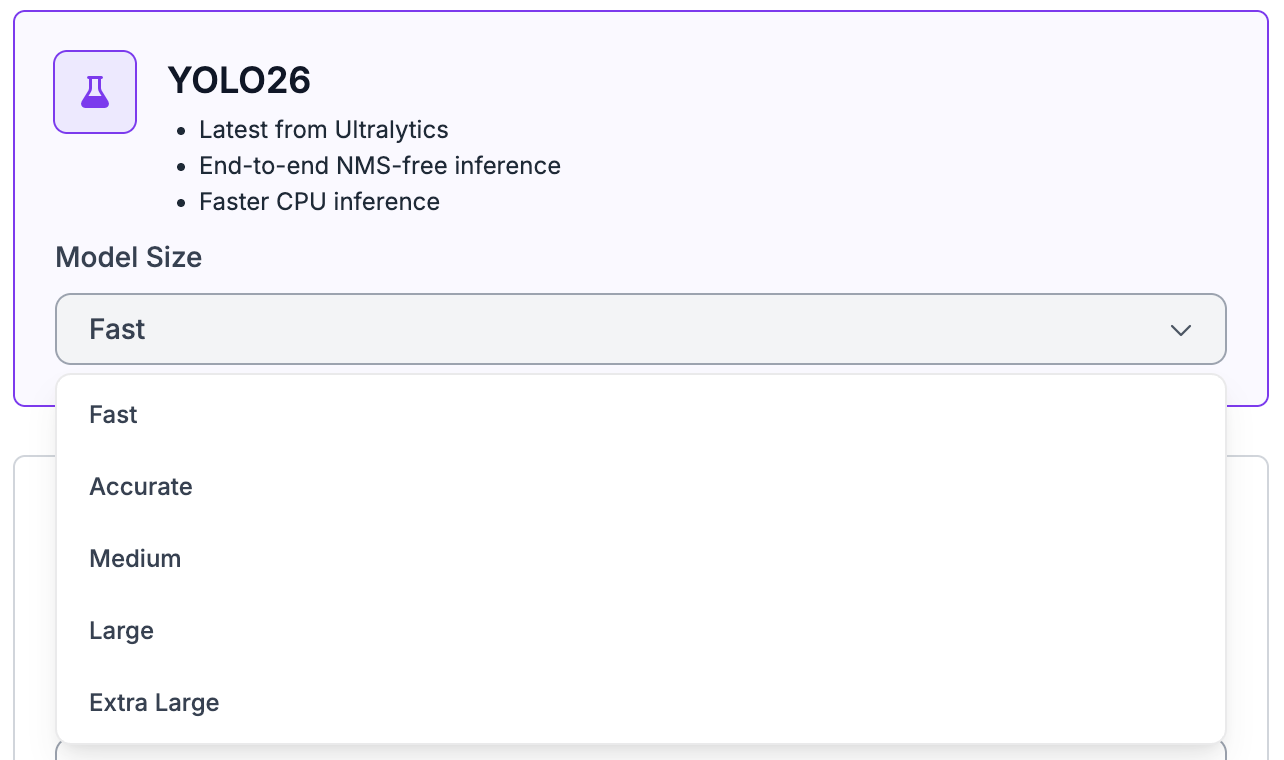
You can start training from the official YOLO26 COCO checkpoint or use a checkpoint from a previous training run in your workspace to improve results iteratively. Once you click Start Training you’ll receive an estimate of the training time. When the job is complete, your model will be ready for deployment across many devices and cloud options.
Label Data for YOLO26
To get started, create a project in Roboflow and upload images. You can then use the Roboflow Annotate interface to draw bounding boxes for object detection or polygons for instance segmentation.
To speed up the process, you can use Roboflow’s AI-assisted features:
- Auto Labeling: Use foundation models to fully automate the labeling process for you.
- Label Assist: Use a pre-trained model (including previous versions of YOLO) to automatically apply labels to your images. You only need to review and correct the annotations, reducing labeling time by up to 50%.
- Smart Polygon: Generate tight polygon masks around objects with a single click, which is essential if you are using YOLO26 for segmentation tasks.
- Collaborative Workflow: Invite your team to label concurrently, leave comments on ambiguous images, and track annotation history to ensure dataset consistency.
Once your images are labeled, you can organize them into a dataset version for export or training.
Export Data in YOLO26 Format
Once your dataset is ready, generate a dataset version. In the export options, you can select the YOLO26 PyTorch TXT format (compatible with standard YOLO formatted data) to download your data for custom training, or train directly in Roboflow.
Roboflow also allows you to convert data from over 40 formats into the format required for YOLO26. Whether you have data in COCO JSON, Pascal VOC, or other formats, you can convert it instantly to the YOLO26 format to try the new model.
Get Started Today
Support for YOLO26 is available now for all Roboflow users. Whether you are building for edge devices that require the new speed optimizations or looking for the latest state-of-the-art accuracy, you can start building with YOLO26 today.
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Trevor Lynn. (Jan 15, 2026). Launch: Train and Deploy YOLO26 with Roboflow. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/yolo26-in-roboflow/
