YOLO models are a family of real-time computer vision models designed to handle a wide range of tasks, including object detection, segmentation, pose estimation, classification, and oriented object detection.
Leveraging popular architectures, these models offer exceptional speed and accuracy, making them well-suited for applications across edge devices, cloud APIs, and more.
In this blog, we’ll examine YOLO26, released January 2026, revealing its key improvements, important features, and how it compares to other leading computer vision models.

What Is YOLO26?
YOLO26 is a multi-task model family designed to handle a broad range of computer vision tasks, including object detection, instance segmentation, image classification, pose estimation, and oriented object detection. The lineup features multiple size variants Nano (N), Small (S), Medium (M), Large (L), and Extra Large (X) to cater to different performance and deployment needs.
Compared to previous YOLO generations, YOLO26 is optimized for edge deployment, featuring faster CPU inference, a more compact model design, and a simplified architecture for improved compatibility across diverse hardware environments. Notable improvements include decreased latency by removing NMS and results staying consistent in fp16 and fp32, making it possible to run the model in an optimized, low-latency way and get the same high accuracy you saw during training.
Try YOLO26 on Images
See how YOLO26 performs on images for common objects included in the COCO dataset. Test out how the model handles your data below.
Download YOLO26
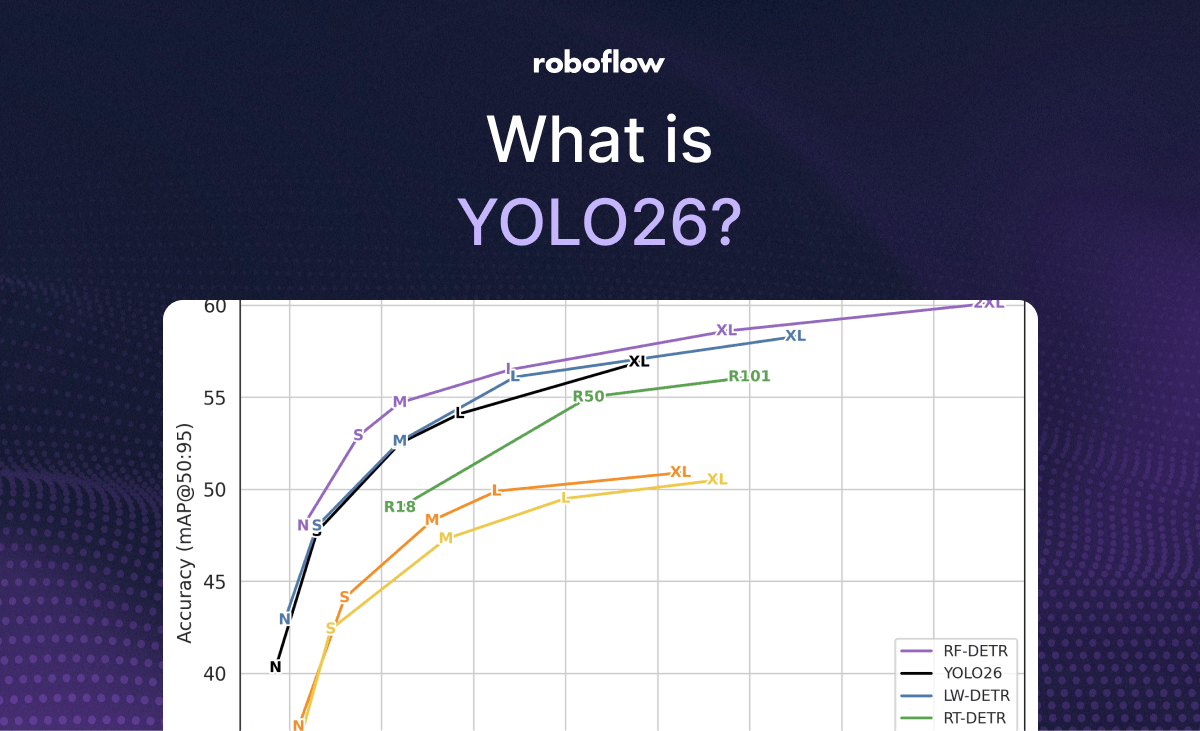
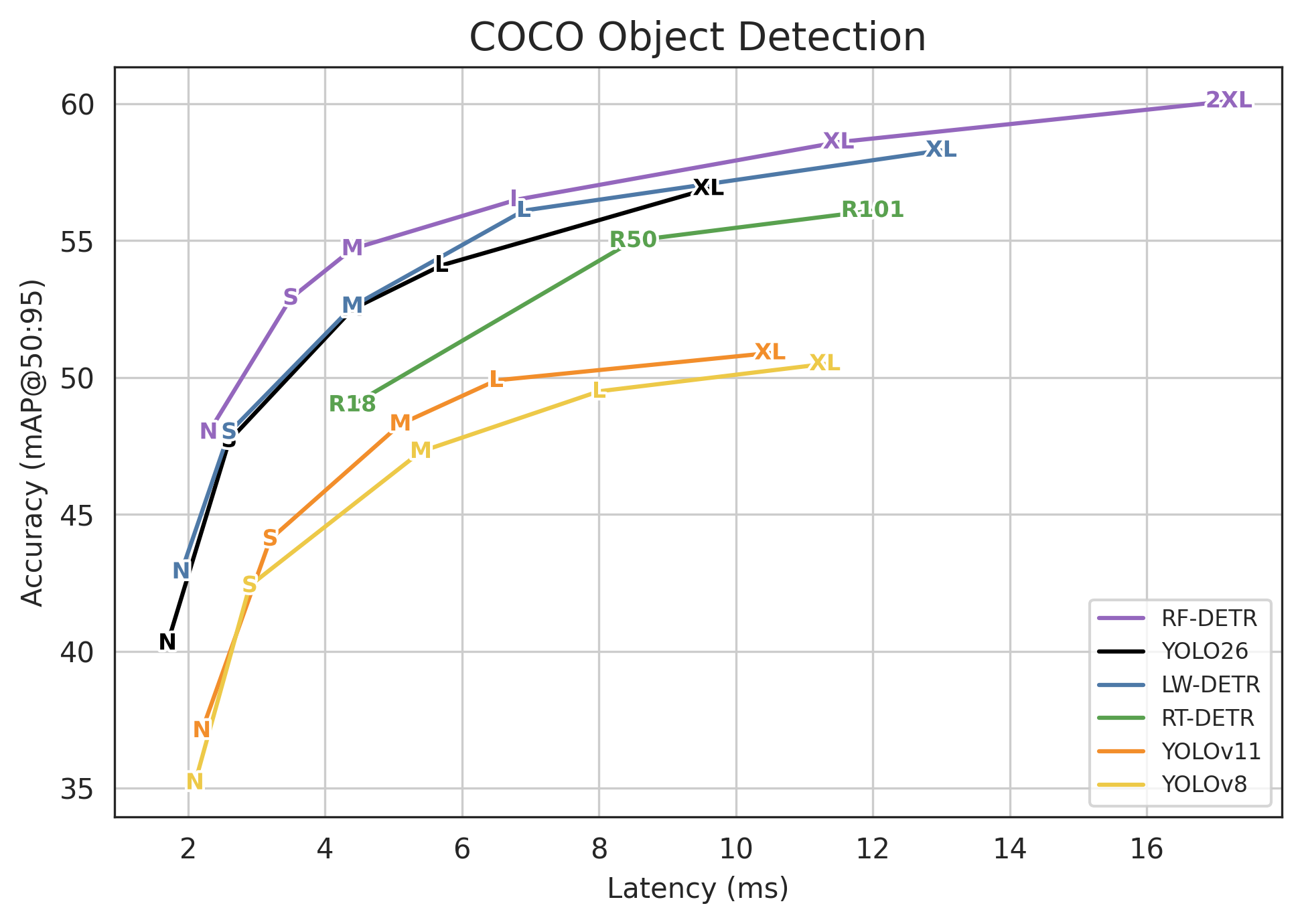
The table below provides links to download YOLO26 for object detection and outlines the Ultralytics reported performance benchmarks for the YOLO26 model family, comparing variants from nano to extra-large across key metrics like accuracy (mAP), latency, and computational cost.
| Model | size (pixels) | mAPval 50-95 | Speed CPU ONNX (ms) | Speed T4 TensorRT10 (ms) | params (M) | FLOPs (B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO26n | 640 | 40.9 | 38.9 ± 0.7 | 1.7 ± 0.0 | 2.4 | 5.4 |
| YOLO26s | 640 | 48.6 | 87.2 ± 0.9 | 2.5 ± 0.0 | 9.5 | 20.7 |
| YOLO26m | 640 | 53.1 | 220.0 ± 1.4 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 20.4 | 68.2 |
| YOLO26l | 640 | 55.0 | 286.2 ± 2.0 | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 24.8 | 86.4 |
| YOLO26x | 640 | 57.5 | 525.8 ± 4.0 | 11.8 ± 0.2 | 55.7 | 193.9 |
This comparison highlights the trade-offs between inference speed and detection precision, enabling you to select the optimal model size for your specific hardware constraints. For other model task types, visit YOLO26 Github.
YOLO26 Architecture
YOLO26 introduces several major improvements including:
- Broader Device Support: It removes the Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) module, simplifying inference, enabling multiple export formats (TFLite, CoreML, OpenVINO, TensorRT, and ONNX), and broadening support for edge and low-power devices.
- Enhanced Small-Object Recognition: It utilizes the ProgLoss and STAL loss functions, improving detection accuracy, particularly for small objects, and providing significant advantages for IoT, robotics, and aerial imagery applications.
- End-to-End Predictions: It eliminates Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) as a post-processing step, producing predictions directly to reduce latency and make deployment in real-world systems faster, lighter, and more reliable.
- Faster CPU Inference: Optimizations in model design and training make YOLO26 faster on CPUs compared to YOLO11. For instance, the YOLO26-N variant delivers up to 43% faster CPU inference than the YOLO11-N, making YOLO26 ideal for real-time performance on devices without a GPU.
- Improved Training: It introduces the MuSGD optimizer, a hybrid of SGD and Muon inspired by Kimi K2 LLM breakthroughs, ensuring stable training and faster convergence by transferring optimization advances from large language models to computer vision.
YOLO26 Alternatives
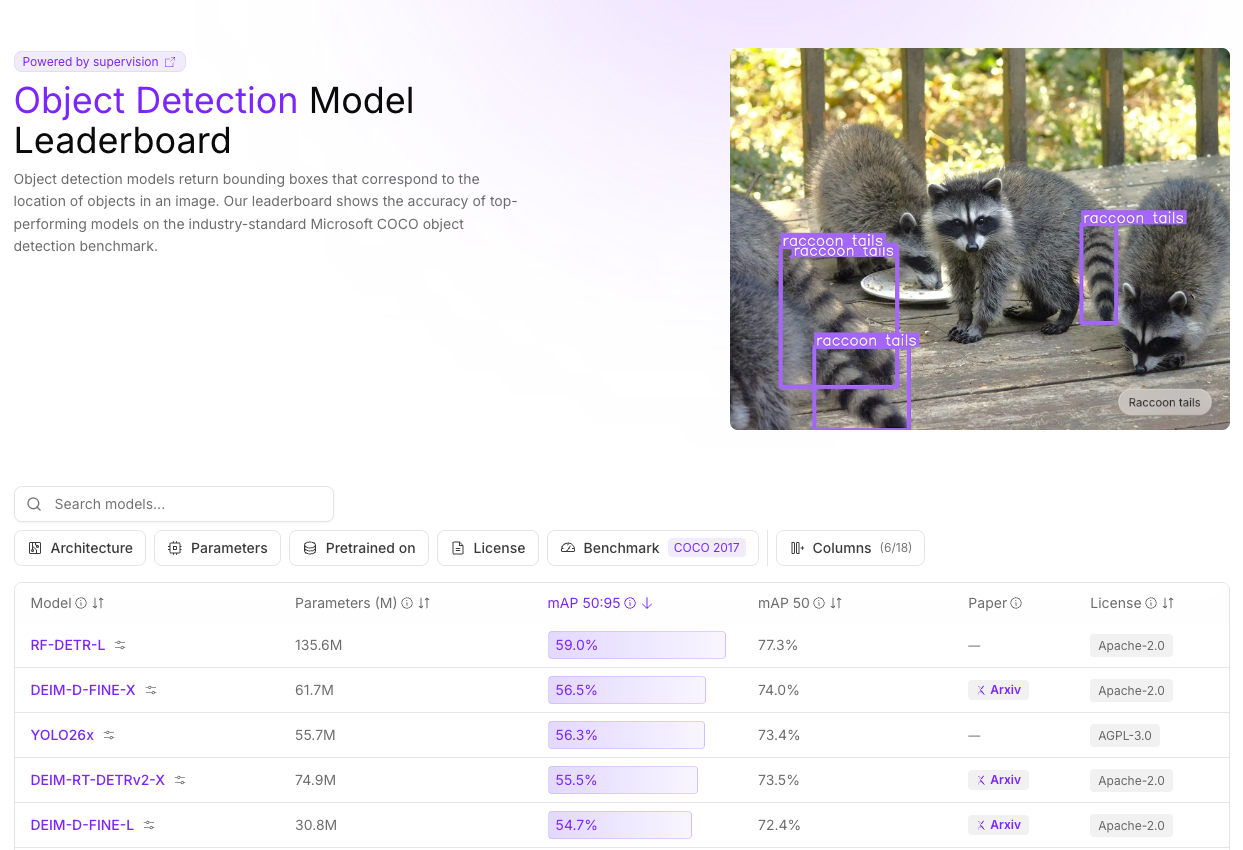
Besides YOLO26, several other multi-task computer vision models are actively used and benchmarked on the object detection leaderboard.
RF-DETR
RF-DETR, developed by Roboflow and released in March 2025, is a family of real-time detection models that support segmentation, object detection, and classification tasks. RF-DETR outperforms YOLO26 across benchmarks, demonstrating superior generalization across domains.
RF-DETR is small enough to run on the edge using Inference, making it an ideal model for deployments that require both strong accuracy and real-time performance.
LW-DETR
Light-Weight Detection Transformer (LW-DETR), released in June 2024, is a real-time object detection architecture that combines the strengths of the Vision Transformer (ViT) and the DETR Decoder.
The model divides images into smaller patches using ViT and integrates multi-level feature representations to produce more accurate and robust predictions. Leveraging this design, LW-DETR outperforms YOLO11 in both accuracy and inference speed.
D-FINE
D-FINE, released in October 2024, is a real-time object detection architecture that introduces a Fine-grained Distribution Refinement (FDR) mechanism to iteratively refine bounding box distributions for greater localization precision.
This refinement process enhances the model’s ability to detect small or overlapping objects while preserving the real-time performance critical for navigation and decision-making applications.
YOLO26 Paper
Ultralytics has not published, and does not plan to publish, a formal research paper for YOLO26. Researchers from Cornell University and Kansas State University did write a paper YOLO26 paper titled: YOLO26: Key Architectural Enhancements and Performance Benchmarking for Real-Time Object Detection
While not an official paper from the creator of YOLO26, it provides a helpful resource for understanding the model.
Conclusion
YOLO26 is an end-to-end, edge-optimized model that supports five core computer vision tasks: object detection, instance segmentation, pose estimation, oriented object detection (OBB), and image classification. The framework offers comprehensive functionality across all these tasks, allowing users to seamlessly perform training, validation, inference, and export for every model variant.
When compared to models such as YOLO11, RF-DETR, LW-DETR, and D-FINE, YOLO26 stands out for its efficient use of parameters and fast inference speed. The removal of the Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) module further enhances compatibility with a wide range of edge and low-power devices.
These enhancements make YOLO26 ideal for edge computing, robotics, IoT applications, and other scenarios with limited computational resources.
Learn more about YOLO models.
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Contributing Writer. (Jan 14, 2026). What is YOLO26? An Introduction. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/yolo26/
