
Computer vision is transforming industries by enabling machines to see, understand, and act on visual data. From optimizing manufacturing lines to enhancing workplace safety, to monitoring transportation infrastructure, AI-powered vision systems are driving efficiency, accuracy, and automation at scale.
Not sure how computer vision might be useful to you? In this guide, we break down 50 practical use cases where businesses are deploying computer vision today. Learn how you can automate sorting, counting, defect detection, read invoices, create a retail planogram, find missing products, track brand logos, detect fires, and so much more.
These examples showcase how vision AI is transforming industries such as logistics, healthcare, agriculture, retail and beyond — and impacting every day lives.
Explore Computer Vision Examples and Real-World Applications
Let’s dive into how computer vision is shaping the future of automation with real-world examples.
1. Automate sorting
Automated sorting with computer vision is a technology-driven process where computer vision systems are used to identify, classify, and sort items or materials based on specific characteristics, such as size, shape, color, texture, barcode, or other visual features. Some examples include defective product sorting, fruit grading, parcel sorting, and pill sorting.
2. Count objects
You can detect and count objects on a conveyor belt using computer vision. In many manufacturing environments, conveyor belts are used for transporting objects, especially small components such as bolts, nuts, or other fasteners through various stages of production. Being able to reliably count these objects in real-time improves inventory management, quality assurance, and overall efficiency.
3. Quality control
With computer vision, you can detect any defects visible to a camera - such as identifying nuanced variations in product specifications like color, texture, inaccurate labels, and other slight imperfections. When a defect is detected, you can trigger automated systems such as removal of a product from an assembly line. Or, if defect rate reaches a defined incidence level, you can alert workers that there may be an issue on the assembly line.
4. Avoid jams
An AI-assisted monitoring system can help avoid costly pileups. Computer vision can continuously track goods moving along the production line, and identify when a component is the wrong size or angled incorrectly. When a problem is detected, it can trigger an alarm for production crews to resolve the issue proactively.
5. Predictive maintenance
Regular maintenance is vital to improving any product's lifetime. By regularly monitoring costly equipment for cracks, changes, rust, and missing pieces, manufacturers can prevent unexpected breakdowns and avoid disruptions in operations.
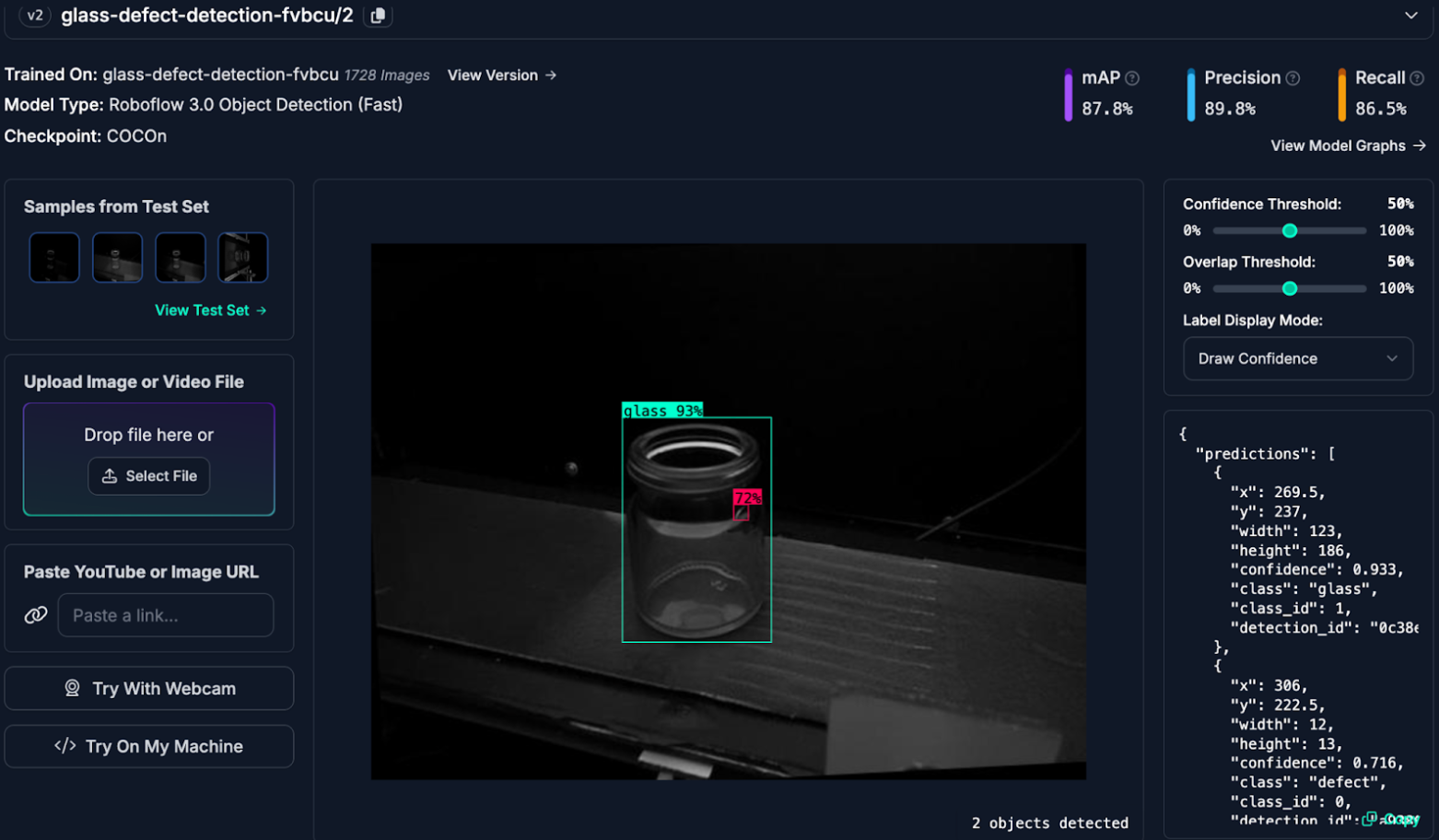
6. Flaw detection
Flaw detection can be used to detect a wide range of defects, including surface defects, structural issues, and material inconsistencies. Surface defects, such as scratches, dents, or blemishes, are visible on the product's exterior. On the other hand, structural issues, like cracks or delaminations, may be internal and require more advanced inspection techniques. A good example is in aviation; external cracks or dents can affect the aerodynamics of a plane. Computer vision systems can quickly process large amounts of data and shorten inspection times. They are also less susceptible to human error and can result in greater accuracy and consistency in flaw identification. Here's how to detect metal defects and ceramic defects using computer vision.
7. Workplace safety
Analyze and detect when a person falls with computer vision. This can be used to identify falls in manufacturing facilities, where a fall may present a significant danger to ongoing operations. Computer vision can distinguish between what is likely to be a fall versus someone kneeling and other voluntary acts that involve being in a non-standing position.
8. Zone monitoring
One potential use of computer vision is to identify when people enter a restricted zone, which could be used to monitor entry into a zone and count the number of people present to ensure the zone does not get too crowded. Learn how to create your own real-time person detection model as well as add zone monitoring abilities to the system.
9. Inspect labels
Label inspection is used on assembly lines, packaging plants, or other industrial environments (such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing), where accurate labeling is crucial for compliance, traceability, and customer satisfaction. Computer vision for label inspection can include ensuring that a label is present on the product; Confirming the label is placed in the correct position on the product; Detecting misaligned labels or verifying the orientation of the label (e.g., not upside-down or rotated); Checking for defects like smudges, blurs, or missing text/images; Validating that the text, barcodes, QR codes, or logos are correct and legible; and Ensuring barcodes or QR codes are readable and match the expected data.
10. Alignment detection
Checking an object's alignment involves making sure it is exactly where it needs to be, and in the correct position and direction. An object's alignment and position can require high levels of precision in various fields. For example, in manufacturing, even a small misalignment can cause defects Similarly, in robotics, accurate positioning is needed for tasks like picking up objects. Luckily computer vision can be used to detect 2D and 3D alignment.

11. Automated color sensing
Automated color detection is more important in our daily lives than we might realize. For instance, it helps factories make sure products look just right by checking for color differences. In cars, it assists with parking and staying in the correct lane. Even your smartphone uses color detection to make photos look better and apply cool filters. With computer vision, you can identify the main colors of an object in an image. You can also count pixel colors.
12. Autonomous drones
UPS Supply Chain Solutions is tracking inventory via autonomous drones. The distribution location where the drones rolled out has a 266,000-square-foot storage area and manages over 930,000 inventory movements annually. The number of hours spent on inventory processes is already down by half at the UPS site.
13. Read paper receipts
Using vision AI models, you can take a photo of a receipt and ask questions to retrieve specific information about a receipt (i.e. how much was spent on a single item); retrieve all text in a receipt; calculate how much tax was added onto a transaction, and more. Learn how to programmatically read receipts with AI.
14. Read invoices
Using models like GPT or Gemini, you can read the text of an invoice and retrieve it as plain text. This information can then be used in business logic. For example, you could build a tool that takes a screenshot of PDF invoices and retrieves specific information, or a tool for digitising old invoices. Learn how to read an invoice with AI.
15. Extract nutrition data from food labels
Accurate nutrition data extraction from food labels is difficult due to the variability of label information, size of labels, and current vision model capabilities. Traditional Optical Character Recognition tools struggle with the complexity and variability of food labels, but Vision Language Models like GPT-4o offer a powerful, context-aware solution. Explore how to build an application that uses a vision-language model to extract nutrition data efficiently and accurately.
16. Create a retail planogram
Retail planograms can help with ensuring every precise detail in a store's layout according to business requirements. By leveraging the use of planograms, retailers can ensure compliance with vendor agreements, measure the effectiveness of price changes, product offers, and more. By leveraging computer vision technologies, retailers and vendors can automate the creation of dynamic and scalable planograms that can be used to ensure products are stacked properly on retail shelves.

17. Automatic stop sign violation detection
This automatic stop sign violation detector utilizes an object detection model fine-tuned in Roboflow, combined with Roboflow’s PolygonZone to identify vehicles that violate stop signs. Video recordings of vehicles that fail to stop are flagged for reporting.
18. Solar roof measurement
For solar businesses and installers, accurately estimating the roof surface area is crucial for planning, costing, and optimizing the number of solar panels that can be installed on a specific house. Traditional methods of roof measurement can be time consuming and labor intensive. However, with advancements in computer vision and the availability of high-resolution aerial imagery, it's now possible to automate this process efficiently.
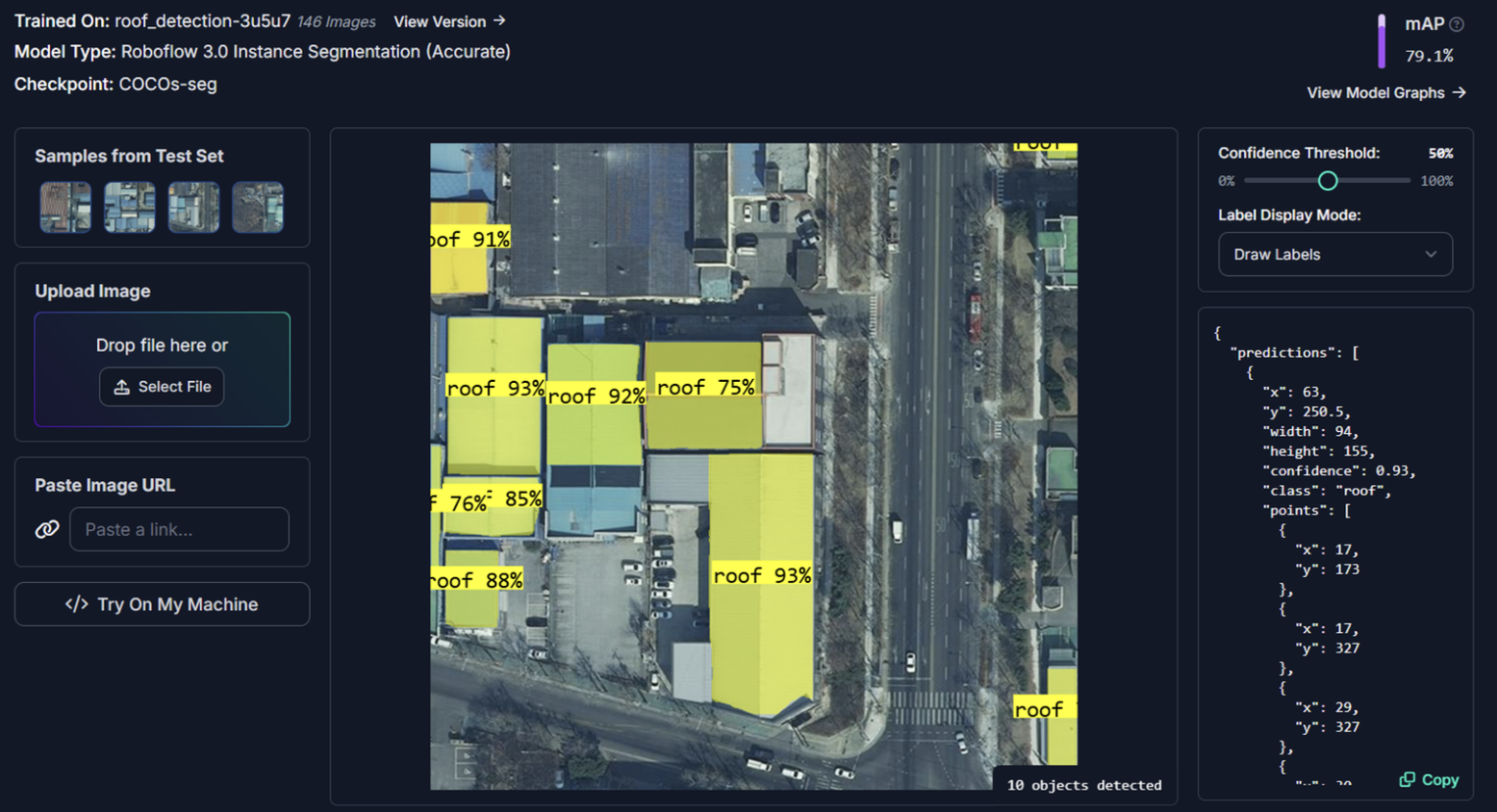
19. Agricultural robots
Vision-enabled robots are used to monitor plant growth, complete harvest tasks, and more. Machines like LaserWeeder are widely used in countries like North America, Europe, and Australia, harnessing computer vision and deep learning to identify and eliminate weeds from croplands.
20. Self-driving cars
Autonomous cars come equipped with advanced driver assistance systems that use computer vision to improve the driving experience. Tesla’s autopilot system consists of eight vision cameras that process 360-degree vision for up to 250 meters. Based on the data gathered from these eight cameras, the hardware can analyze real-world information and detect pedestrians, lanes, and road signs.
21. Warehouse robots
Robots that use computer vision can be useful in inventory management, warehouse navigation, and package sorting applications. For example, Amazon uses autonomous robots, like Proteus, in its warehouses to manage large packages weighing up to 800 pounds, moving them from inventory to shipping areas.
22. Count objects that cross lines
Computer vision makes it simple to create a line counter to count any object. For example, you can monitor traffic by creating a line counter that increments as cars cross a given point. Learn how to build an application that counts how many cars cross a given point in a video.
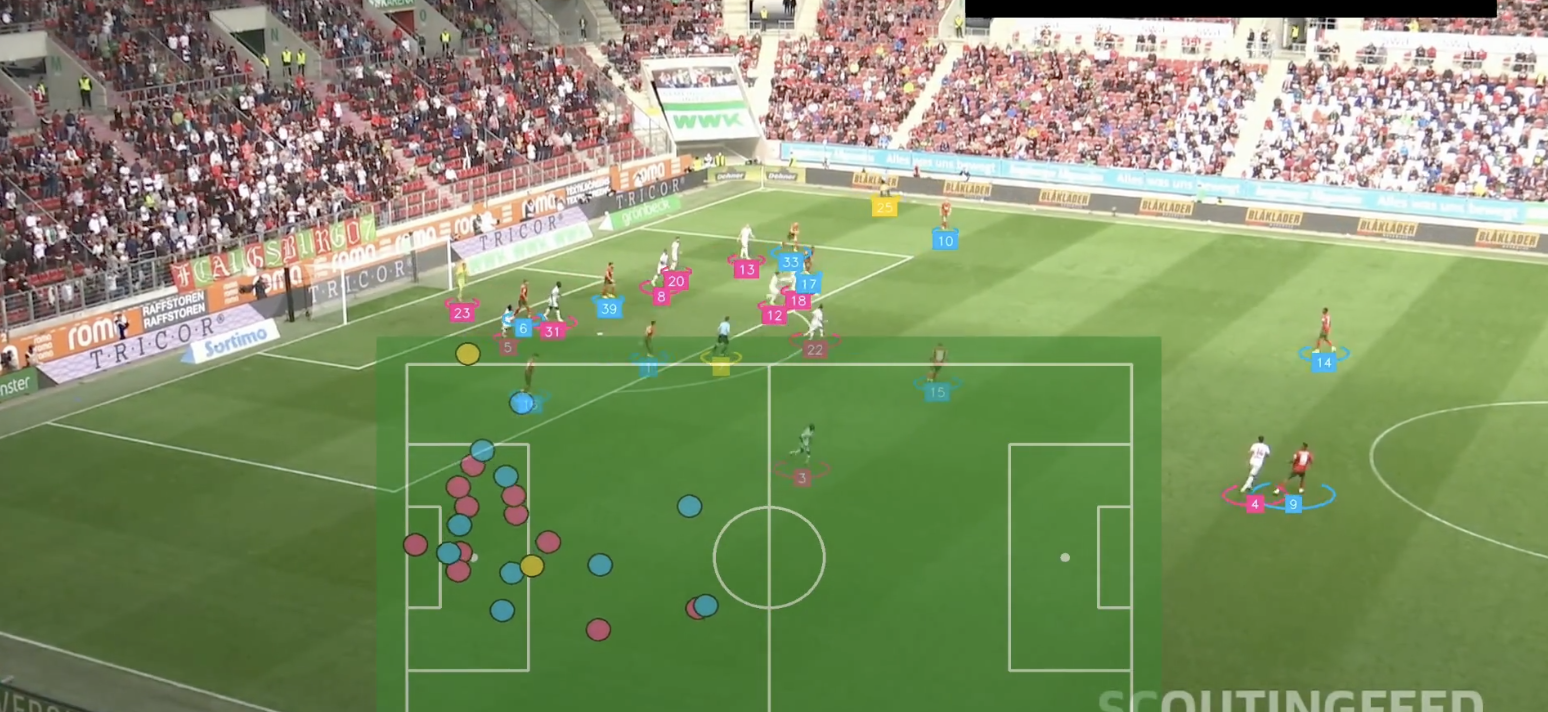
23. Ball and player tracking in sports (foot path tracking in retail stores, as well)
Computer vision in player and ball tracking has become a very powerful tool in sports analysis. Whether it's football, basketball, or cricket, such tracking systems can be used to record precise 3D trajectories, predict ball paths, and even identify player interactions, providing valuable insights into the performance of the players, team strategies, and game dynamics. A new computer vision-based system, known as semi-automatic offside technology (SAOT), was introduced at the 2022 FIFA World Cup. The technology is now being used for the 2024-2025 English Premier League.
24. Remove an image's background
Are you working on a poster or card, and need the background of an image removed? You can actually do that with computer vision. Learn how to build your own custom background removal application using computer vision.
25. Blur your computer screen
You can even use computer vision techniques to automatically blur your screen during sensitive moments, such as when switching between tabs or browsers. This could be used by live streamers to blur a screen while switching tabs, reducing the chance a tab is accidentally opened with sensitive information visible.
26. Count eggs
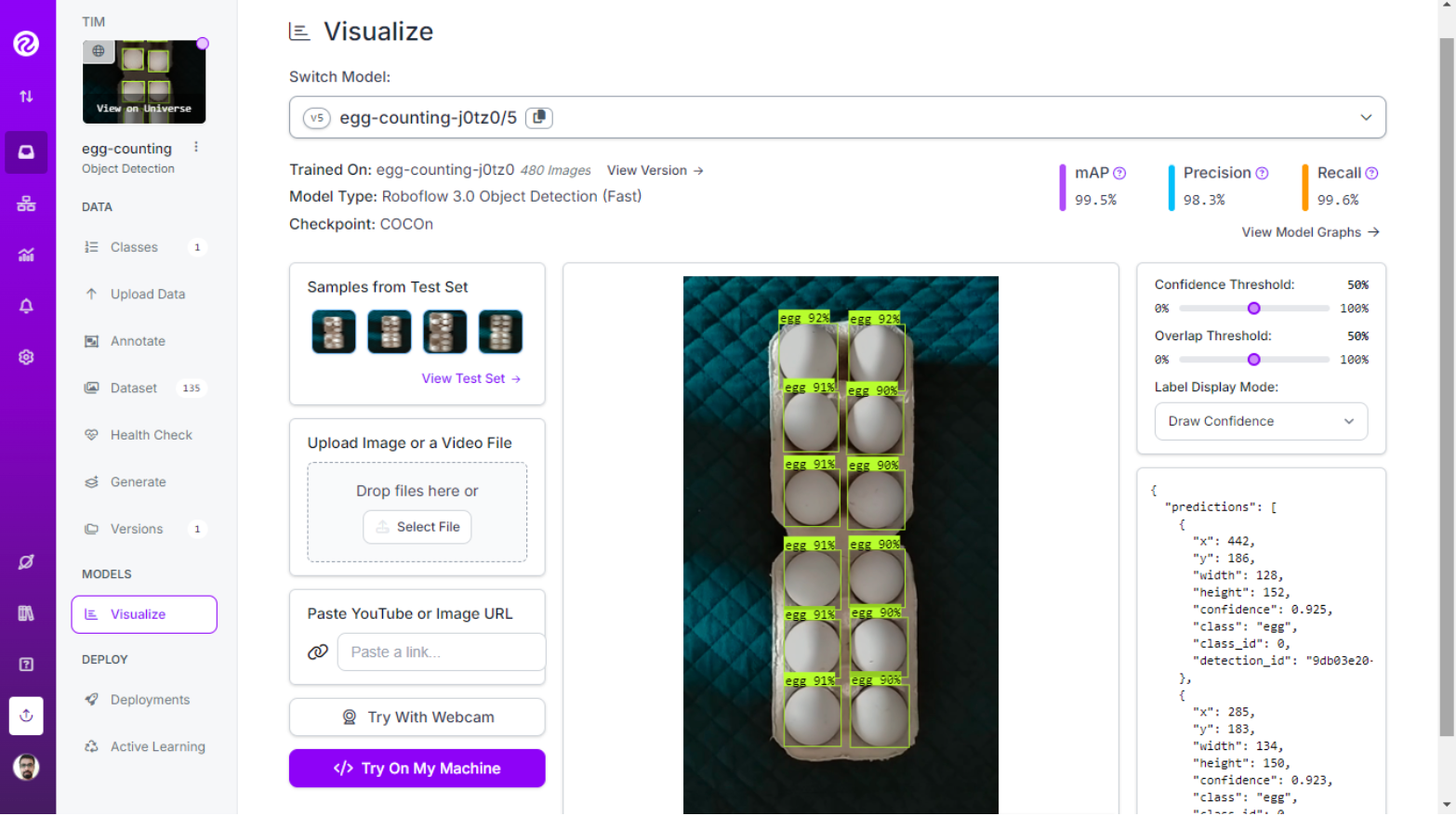
Computer vision can be used to create an egg counting and tracking system. Easily monitor and count eggs at home (or any other place where inventory is required), helping you maintain an accurate inventory and automatically placing orders when the quantity is low.
27. Workout pose correction
Computer vision is a useful tool when it comes to understanding and quantifying real-world activity happening in real-time. Tracking human movements with pose estimation is a common way to evaluate athletics or general body movement to help gain insight into proper form and technique. Learn how to use keypoints or pose estimation models for building custom computer vision applications.
28. Make a reading assistant
Readers can face trouble when encountering new, unfamiliar words. You can use computer vision to create an interactive reading assistant that detects specific words in an image and reads them aloud using GPT-4. That way, readers can hear the word which helps with knowing what the word may be as well as with pronunciation.
29. Plant disease detection
Early detection and diagnosis of diseases affecting plant leaves can significantly reduce crop losses and improve productivity in agricultural environments. As just one example, computer vision can be used to predict tomato leaf diseases.
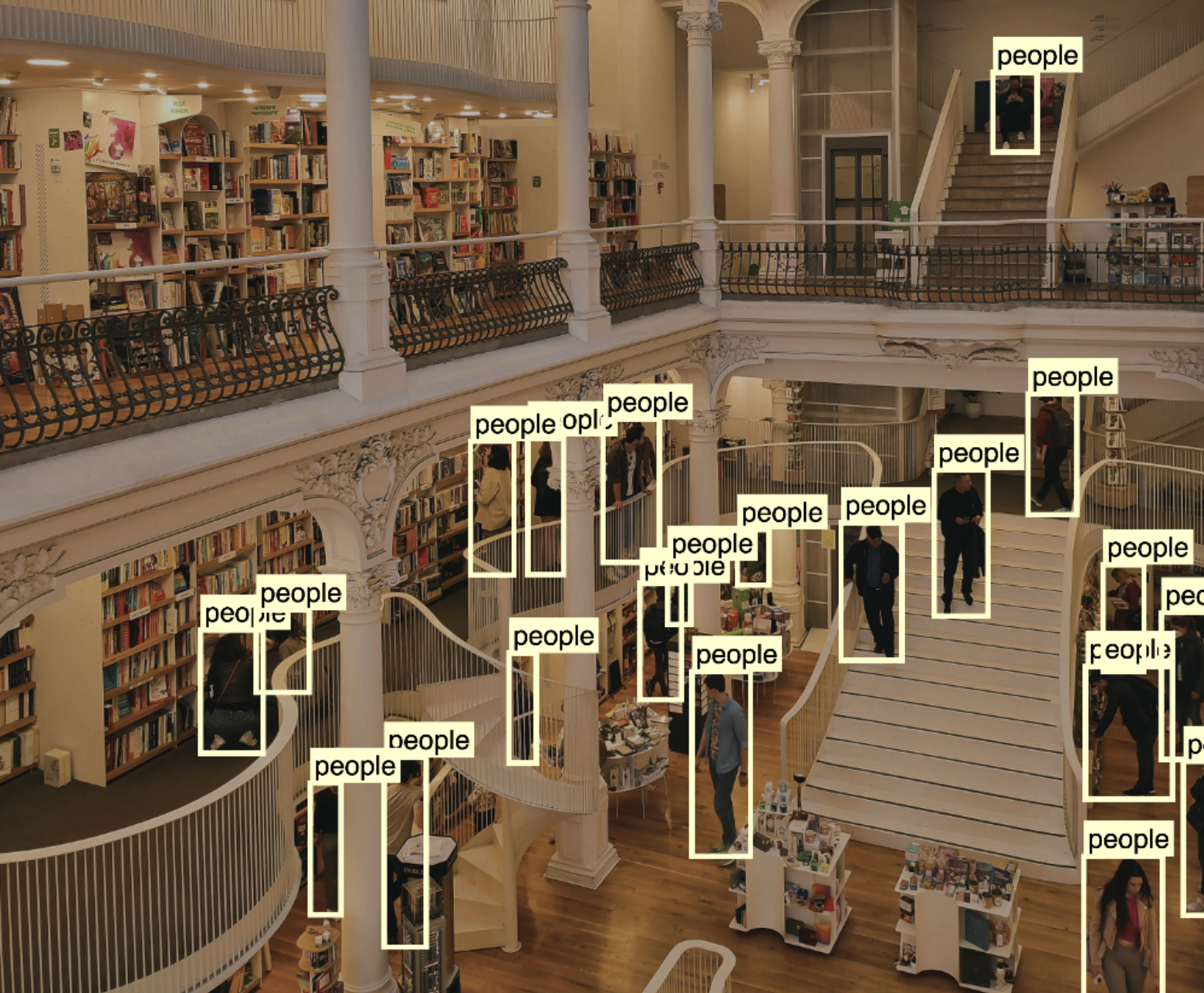
30. People counting for security
Counting and keeping track of a large number of people entering and exiting an event can be challenging, especially when security is a priority. Traditional methods of monitoring people make it difficult for security officials to keep track of everyone in real-time. Counting people using computer vision is a great way to analyze how many people are in a particular area.

31. Extract data from tables
Extracting specific text or structured information from scanned documents or images used to be an incredibly difficult challenge. With the advent of models like Claude, however, it is easier than ever to retrieve data such as the contents of tables from a document.
32. Automate rebar counting
Manual rebar counting is a time-consuming task and prone to errors and inconsistencies. But, you can automate rebar counting with computer vision. You can use a fine-tuned computer vision model to count individual pieces of rebar, useful for building inventory management and quality verification system.
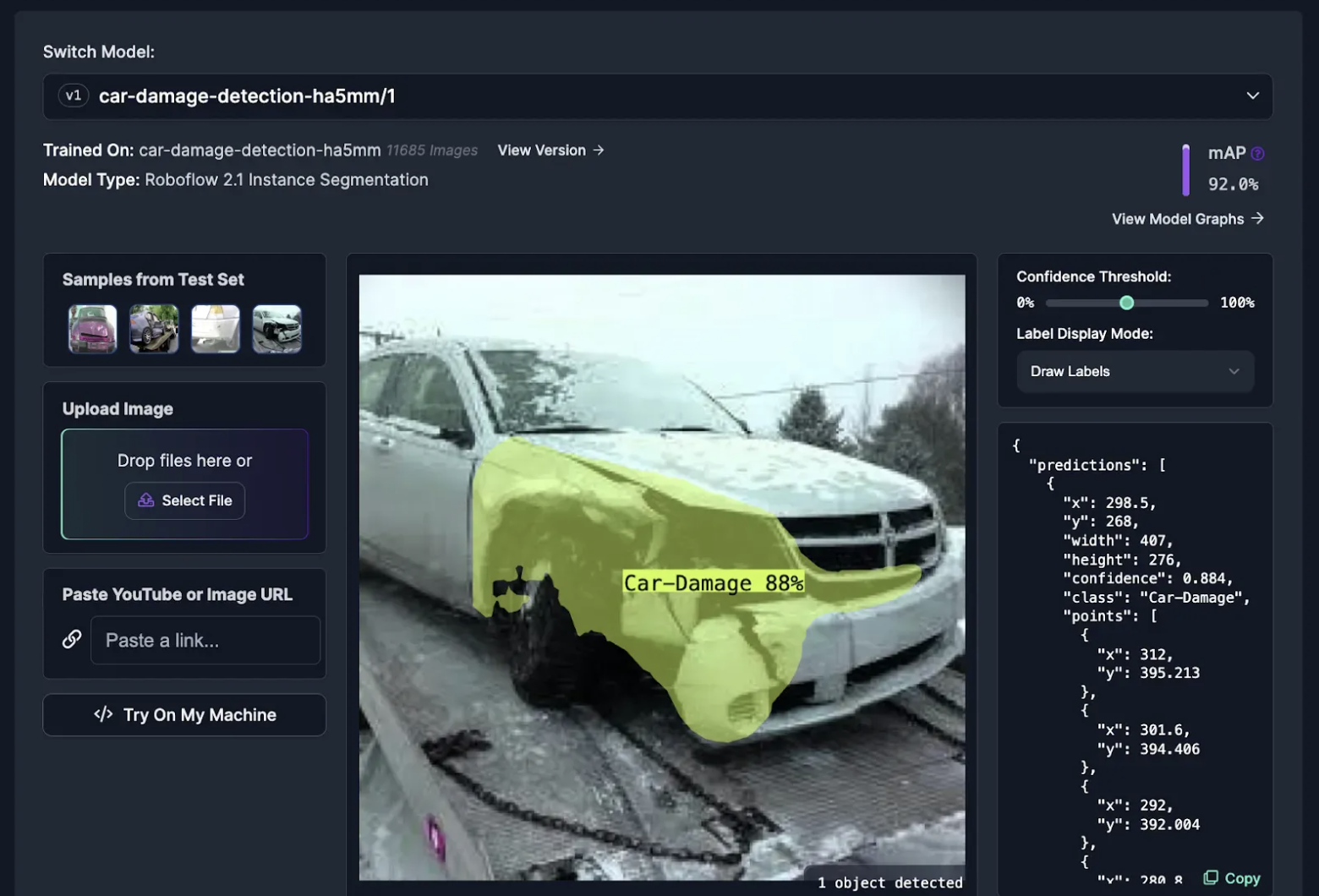
33. Assess car damage
Using computer vision, you can identify visual defects with vehicles. This could be used as part of an inspection system at a car manufacturer, for use in helping to calculate the value of second-hand cars based on any visual damage, and more. Using cameras and AI, computer vision can instantly analyze photos of your car damage, identifying the issue and even estimating the severity.
34. Measure objects
Measuring the dimensions of objects is important in executing pass/fail inspections, particularly in environments where high value goods or a high volume of goods are being produced and distributed. With computer vision you can automate the dimension inspection process in dynamic environments by segmenting the item of interest and returning the width, length, and height in your unit of measurement choice. Learn how to measure the size of fish. And, speaking of fish, Tidal is using computer vision to monitor salmon farms to catch potential issues — like sea lice — before they do serious damage.
35. Inspect chocolate boxes
When you are preparing boxes of chocolates on an assembly line, it is essential that every box meets your specifications. There should be the correct number of chocolates, boxes should be in the correct order per the intended arrangement for the box, And chocolates should be in good condition; not slightly melted, not scratched. You can use computer vision to conduct various visual inspections on chocolate boxes.
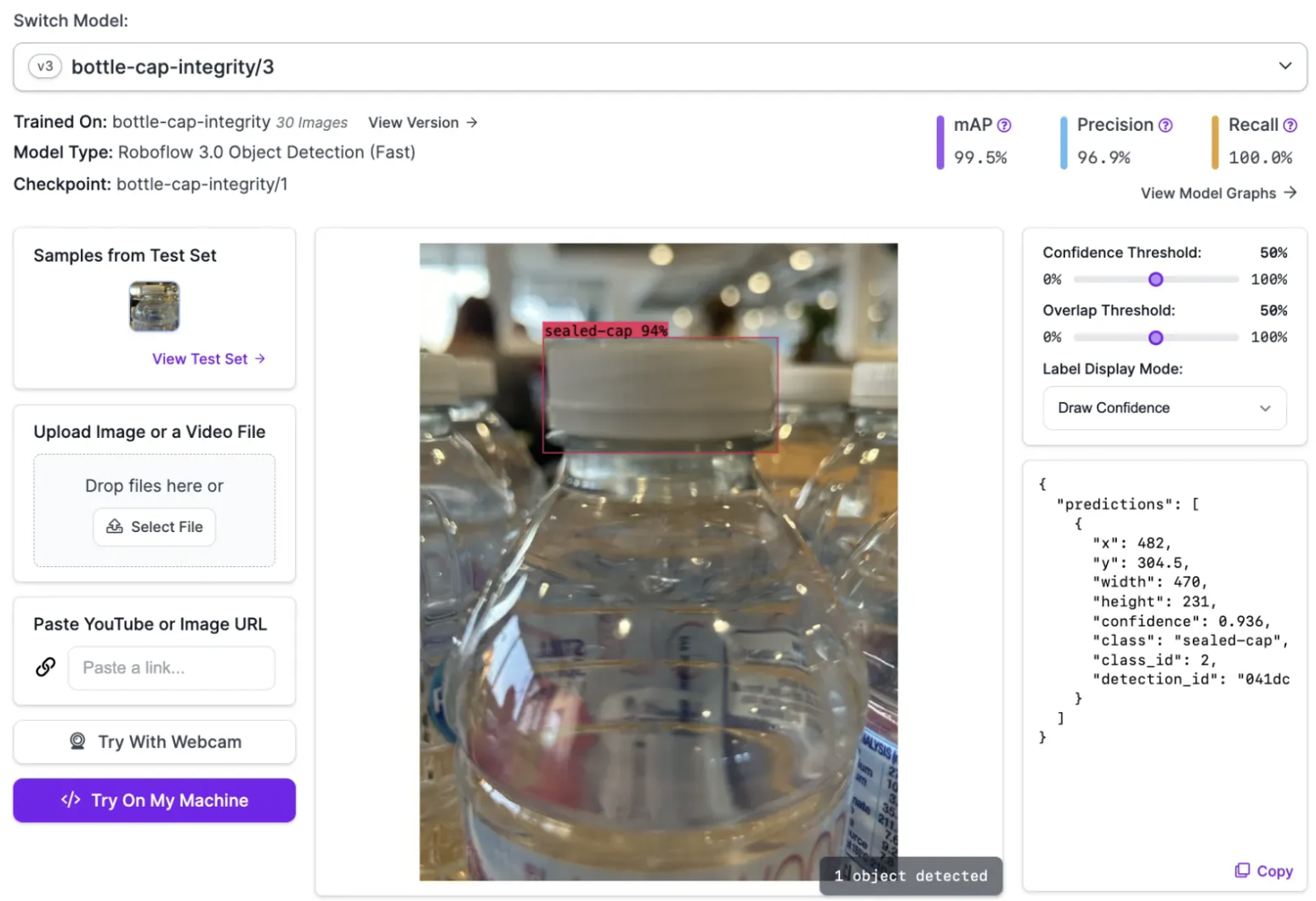
36. Inspect bottle caps
Before bottles can be packaged for distribution, inspections must be run to assure the integrity of the bottle cap. If a bottle cap is not properly sealed, it must be rejected before proceeding to packaging and distribution. Computer vision can be used to identify whether a cap is or is not properly sealed, and check whether there is or is not a cap present on a bottle. Here's how to build a bottle cap inspection system that verifies the integrity of a bottle cap.
37. Pill counting and identification
Computer vision can be used to detect, identify, and count pills. Pills are small, and can often be difficult to identify as a result. Counting individual pills can be both tiresome and tedious, placing strain on already thin-stretched healthcare employees. The consequences of misidentification, and therefore misadministration, of medicines can be catastrophic.
38. Sterile processing of healthcare tools
Sterile processing is another process that depends on traceability to ensure that hospitals run smoothly. Sterile processing that is not carried out effectively can be negative for patient care and costly for hospital systems. Between cleaning and decontamination, packaging, sterilization, and distribution, computer vision can be deployed to streamline this process.
39. Personal protective equipment monitoring
Computer vision models can be deployed to first detect the presence of proper PPE use on individuals within a hospital setting, like the waiting area of an emergency room, and then blur the faces of individuals in the frame to ensure that privacy is maintained. These analytics can be used by operations specialists to better allocate resources and ensure that proper PPE use is being observed.
40. AI-Assisted cancer screening
A well-trained computer vision model has the ability to detect cancerous cells that may have gone undetected by medical professionals. When a computer vision model is deployed in this way as a second check after an initial diagnosis from a doctor, it can encourage doctors to take a second look at an image when a model finds potentially cancerous cells.
41. Missing item inspection
You can use computer vision to count the number of products present in packaging. This is ideal for assuring the count of food and drink product packaging. For example, you can implement a check that ensures a box contains 12 bottles before being sealed and prepared for distribution. If a box doesn’t contain the right number of bottles, it can be sent for additional processing. Learn how to build a missing item inspection system with computer vision.
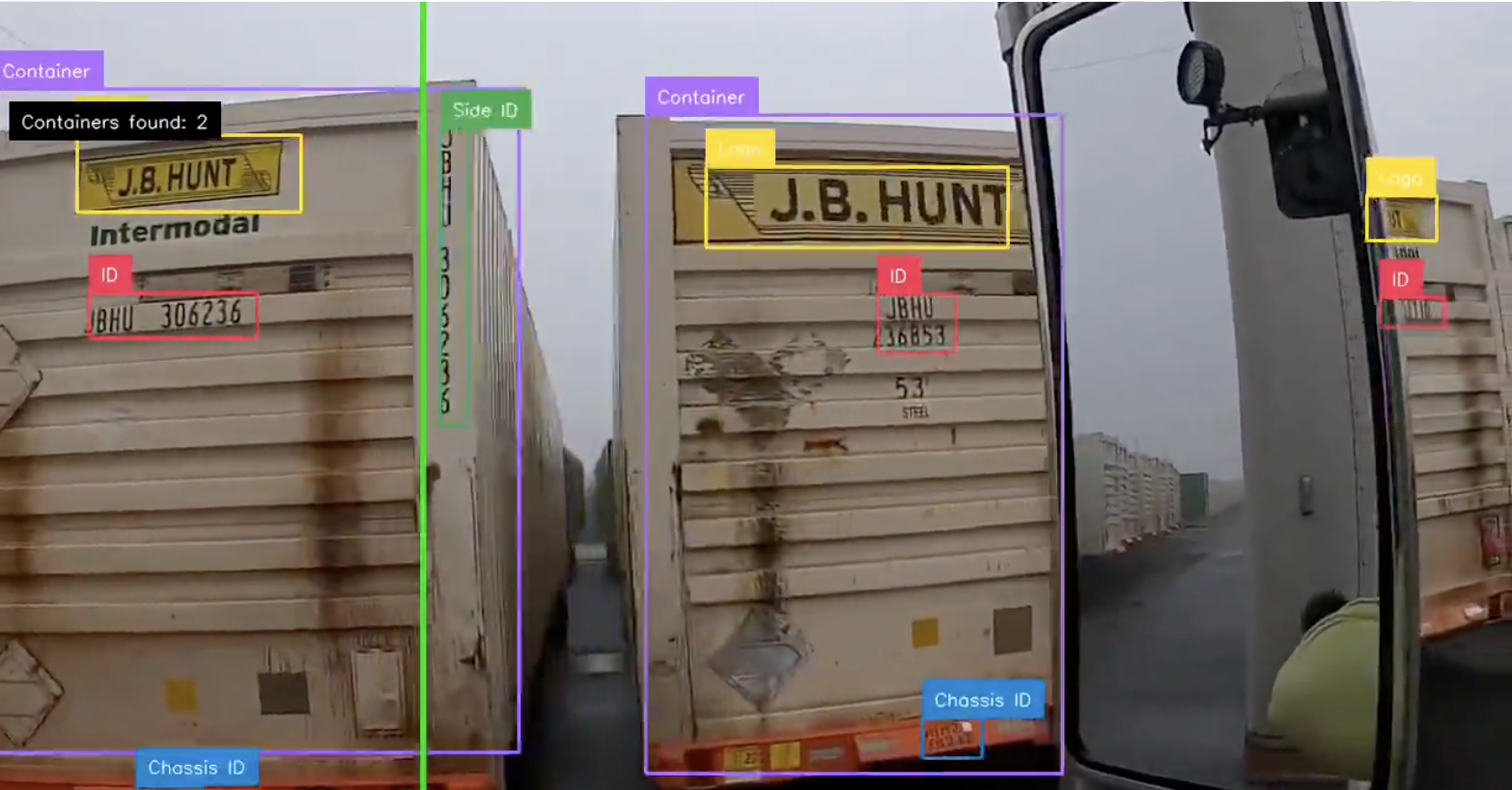
42. Yard management
Using computer vision, you can accurately track intermodal containers in a yard. For example, by adding a camera to any hostler truck, you can passively collect container location data for a continuous stream of real-time information. The footage from this camera can then be processed to retrieve the chassis ID, container ID, container brand, and any other visual information you need to record. See how to build a yard management system with computer vision.
43. Detect speed
You can even estimate the speed of vehicles using computer vision. Explore the entire process, from object detection to tracking to speed estimation, in this tutorial.
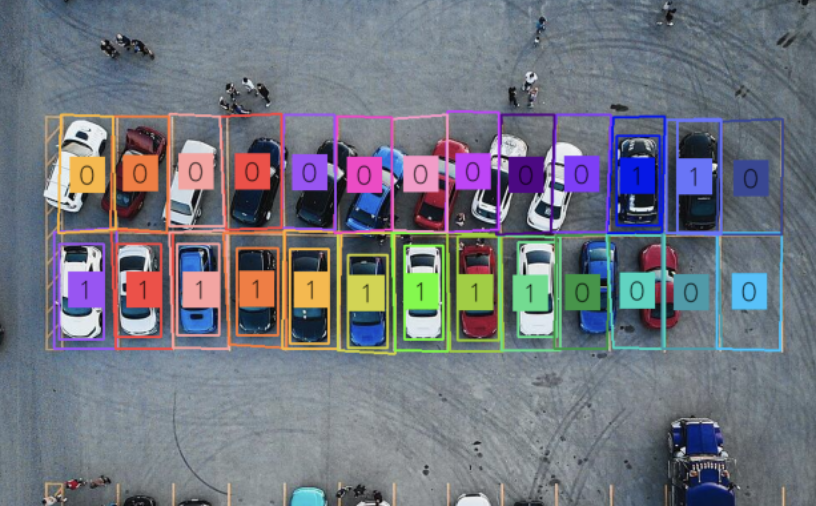
44. Smart parking
We spend a lot of our time commuting from place to place, and parking is always a hassle. For example, finding a parking spot at the mall when you go shopping can be a frustrating task. With that said, cameras and computer vision algorithms can work together in parking lots to know if a vehicle has occupied a parking space or not. Learn how object detection can be used in parking management systems.
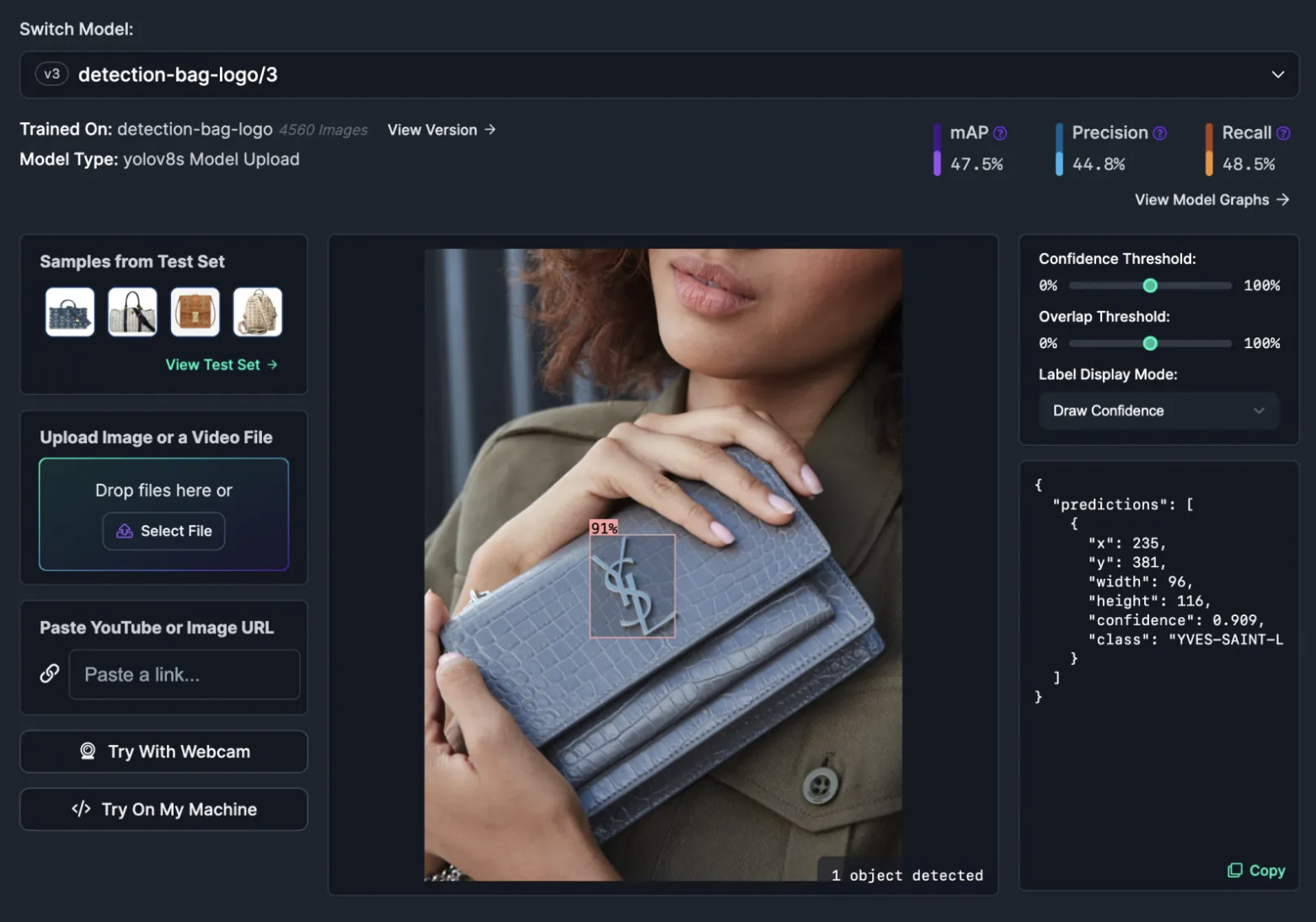
45. Track brand logos
With computer vision, you can detect brand logos in images or videos. A computer vision solution enables you to find when a brand is on screen in a video, and for how long the brand is on screen. This information can be used by brands to quantify their reach, advertising providers and broadcasters to verify that sponsorship requirements for on screen time have been met, to ensure brand logos do not appear in specific scenes (i.e. when someone is smoking), and more.
46. Monitor plant growth
Measuring plant growth is essential for several reasons in agricultural, ecological, and scientific contexts. For example, plant growth metrics provide valuable information for use in optimizing crop yield, managing ecosystems, studying environmental changes, and conducting research in plant biology. In the field of biotechnology, researchers use plant growth measurements to assess the effects of genetic modifications and to develop crops with improved traits, such as resistance to pests, diseases, or environmental stress. Learn how computer vision can be used to monitor plant growth.
47. Aerial fire detection
Traditional fire detection technologies frequently rely on ground-based equipment or satellite imaging, which might have limitations in terms of accuracy, speed, and coverage. To address the rising hazard of wildfires, computer vision can be used. Computer vision can allow earlier detection of wildfires when deployed using across large swathes of forest that would be difficult for humans to monitor every day. Learn how to detect fires using aerial imagery.
48. Online exam proctoring
Online proctoring systems play a critical role in ensuring fair and honest evaluations of students' knowledge and skills in remote settings. Some students may be tempted to use their smartphones during these assessments, making it essential to detect and prevent this behavior. You can build an application that uses computer vision to create an online proctoring system.
49. Chess game recorder
A chess set with sensors costs ~$500 USD! This price tag is not very accessible for everyday chess players or local chess clubs. With computer vision you can make a smart chess recorder that can record and analyze your chess games.
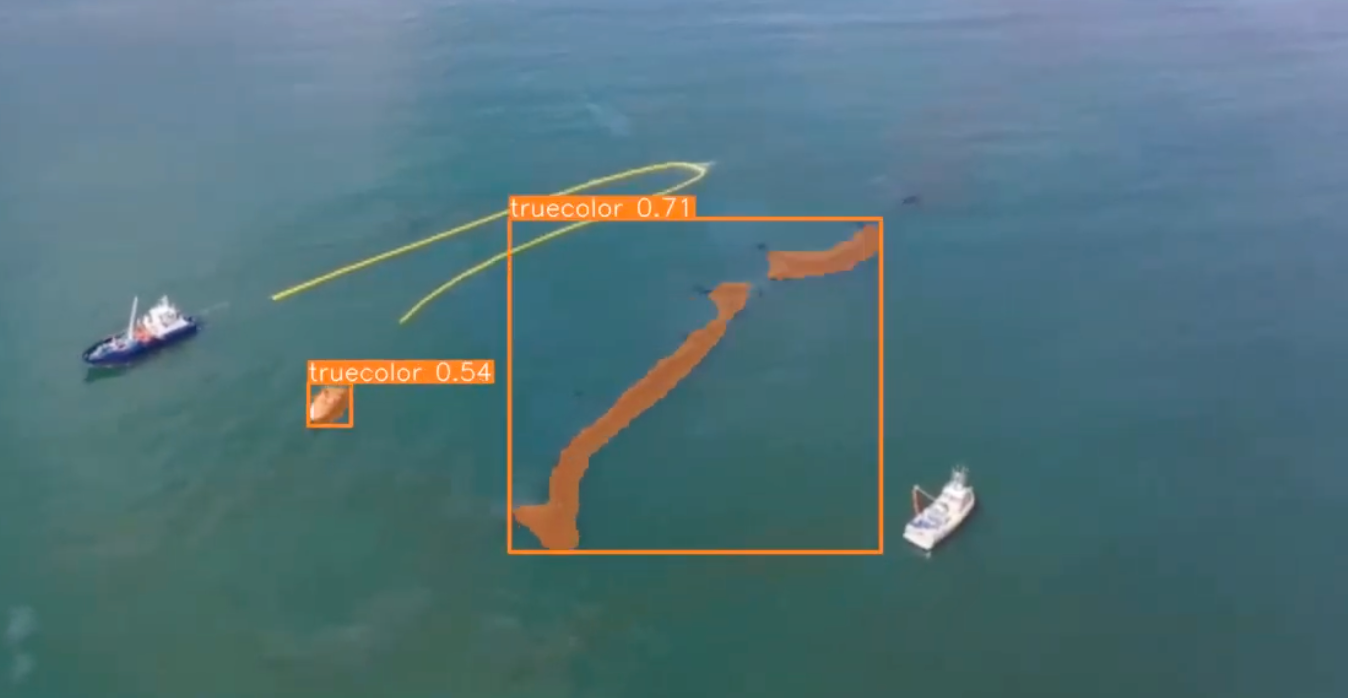
50. Detect oil spills
Due to the logistical difficulties in getting to impacted areas, cleaning up an oil spill is an expensive endeavor. Before sending out a clean-up crew, it is essential to precisely measure the spill's characteristics, such as the volume, thickness, and extent, in order to maximize resources and save costs. This is where computer vision becomes an essential tool to detect oil spills.
Apply Computer Vision Examples To Your Business
Computer vision is transforming industries by automating complex visual tasks, improving efficiency, and reducing errors. From streamlining aerospace operations to quickly verifying government documents, and even automating security procedures for oil rigs, the many uses of vision AI continue to expand.
With accessible tools and pre-trained models, businesses can now integrate computer vision into their workflows faster than ever. As you've seen, the right vision AI solutions can drive significant improvements in cost, speed, and accuracy.
At Roboflow, we’re dedicated to helping teams unlock the full potential of visual AI. Ready to build your own AI applications? Get started today with our enterprise platform or talk to an AI expert to learn more.
Cite this Post
Use the following entry to cite this post in your research:
Trevor Lynn. (Feb 13, 2025). 50 Computer Vision Examples and Real-World Applications. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/computer-vision-examples/
